Figure 4. Effect of ddc2-S4 on Mec1-Ddc2 interaction and Mec1 localization.
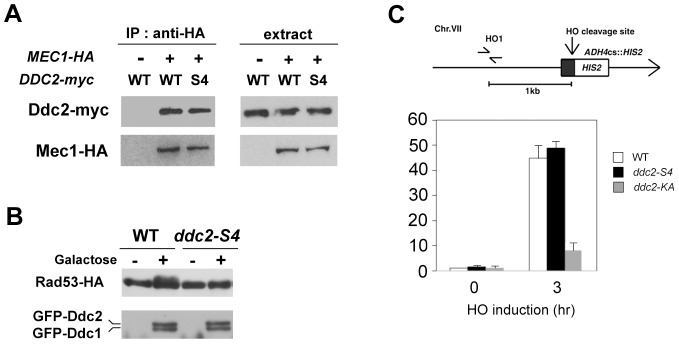
(A) Effect of ddc2-S4 mutation on Mec1-Ddc2 interaction. MEC1-HA ddc2Δ (KSC1340) or ddc2Δ (KSC1234) cells were transformed with YCp-DDC2-myc or YCp-DDC2-S4-myc. Extracts prepared from cells were subjected to immunoprecipitation with anti-HA antibodies. Immunoprecipitates and whole extracts were analyzed by immunoblotting with anti-HA or anti-myc antibodies. (B) Effect of ddc2-S4 or ddc2-KA mutation on Mec1 localization to an HO-induced DSB. Wild-type (KSC1635), ddc2-S4 (KSC2158) or ddc2-KA (KSC2159) cells expressing Mec1-HA were transformed with the YCpA-GAL-HO plasmid. Transformed cells were grown in sucrose and treated with nocodazole. After arrest at G2/M, the culture was incubated with galactose for 3 hr to induce HO expression, while half of the culture was maintained in sucrose to repress HO expression. (Top) The strains contain an HO cleavage site, marked with HIS2, at the ADH4 locus on chromosome (Chr.) VII. The HO1 primer pair amplifies a region 1 kb away from the HO cleavage site. An arrow represents the telomere. (Bottom) Cells were subjected to chromatin immunoprecipitation with anti-HA antibodies. Association of Mec1 with an HO-induced DSB was analyzed by real-time PCR. Relative enrichment was determined from three independent experiments. (C) Effect of ddc2-S4 on Rad53 phosphorylation after co-localization of Ddc1-LacI and Ddc2-LacI to a LacO array. Cells containing the LacO256 array and RAD53-HA with the combination of DDC1-LacI-GFP and DDC2-LacI-GFP (CBY88) or DDC2-S4-LacI-GFP (KSC2419) under the control of GAL promoter were grown in sucrose and arrested in nocodazole for 2 hr. Galactose was pulsed for 2 hr, and then cells were further incubated with glucose. Samples were collected at 2 hr after addition of glucose and subjected to immunoblotting analysis with anti-HA or anti-GFP antibodies.
