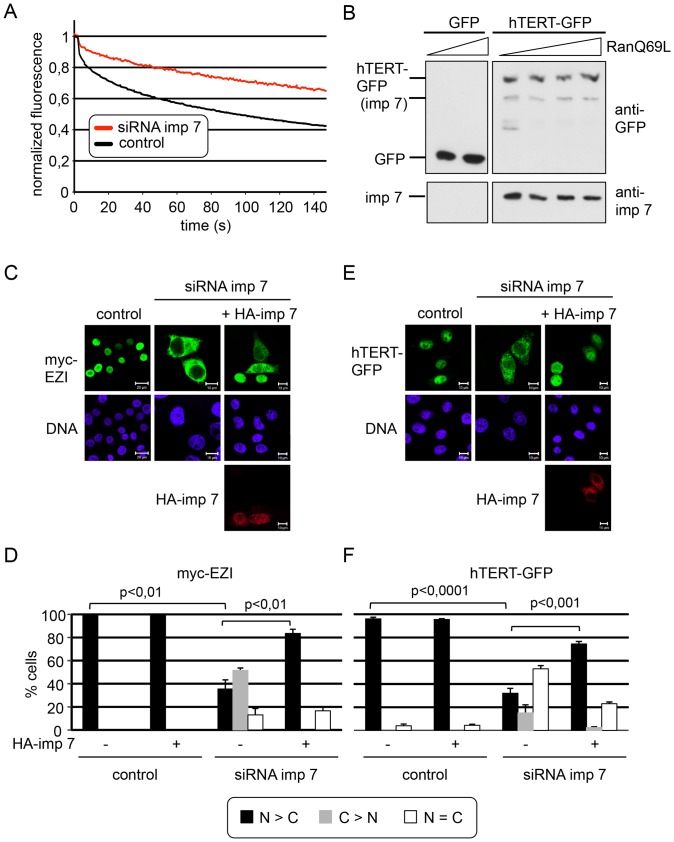
Figure 3. Importin 7 functions as an import receptor for hTERT.
A, HeLa cells expressing hTERT-GFP that had been treated with either control siRNAs or with siRNAs against importin 7 were analyzed for the dynamics of nuclear import of the reporter protein by FLIP. The graphs show the mean loss in fluorescence in three independent experiments, analyzing a total of 45 cells per condition. Error bars were omitted for clarity (see Fig. S1 for the identical experiment with error bars). B, HEK 293 cells were transfected with constructs coding for GFP or hTERT-GFP. Cell lysates were subjected to immunoprecipitation using immobilized anti-GFP-antibodies (“GFP-trap”). Reactions contained increasing amounts (0, 10 µg/ml for GFP and 0, 2.5, 5, 10 µg/ml for hTERT-GFP) of RanQ69L that had been preloaded with GTP. Precipitated proteins (GFP, hTERT-GFP and importin 7) were analyzed by immunoblotting. The weak signal for importin 7 (imp 7) in the upper panel results from the initial detection of the import receptor on the same blot (lower panel). C-F, Overexpression of exogenous importin 7 rescues nuclear import of hTERT-GFP. HeLa cells were treated with control siRNAs or with siRNAs against importin 7 and transfected with plasmids coding for either myc-EZI (C, D) or hTERT-GFP (E, F), alone or together with a plasmid coding for HA-importin 7, as indicated. Cells were fixed and analyzed by fluorescence microscopy. myc-EZI and HA-importin 7 were detected using specific antibodies against the myc- and HA-tag, respectively. Bars, 10 µm or 20 µm (control in C). D, F, Quantification of the results shown in C and E. Error bars depict the standard deviation from the mean of at least three independent experiments.