Figure 1.
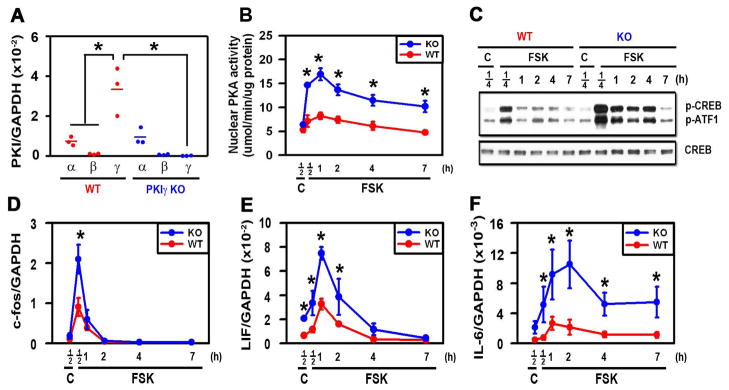
PKIγ deletion substantially extends PKA signaling following stimulation with FSK. MEFs from wild type (WT) and PKIγ−/− (KO) mice were incubated for 12 hours in osteogenic medium (A) or for the indicated times (B–F) in osteogenic medium containing 1 uM forskolin (FSK) or 0.1% DMSO as a vehicle control (C). mRNAs encoding members of the PKI family (A) and PKA-dependent genes (D–F) were measured by quantitative real-time RT-PCR, nuclear PKA activity was assessed biochemically (B), phosphorylation of CREB and ATF-1 and total CREB were assessed by Western blotting (C). * denotes p < 0.05 as compared with the indicated groups (A) or the WT groups at the same time points (B, D–F). In (A), the horizontal bars represent the means of the 3 independent experiments indicated by the individual symbols that represent means of 3 culture wells/group, each assayed in triplicate. In (B, D–F), the symbols represent the mean ± SD of 3 independent experiments, each consisting of 3 culture wells/group, each assayed in triplicate.
