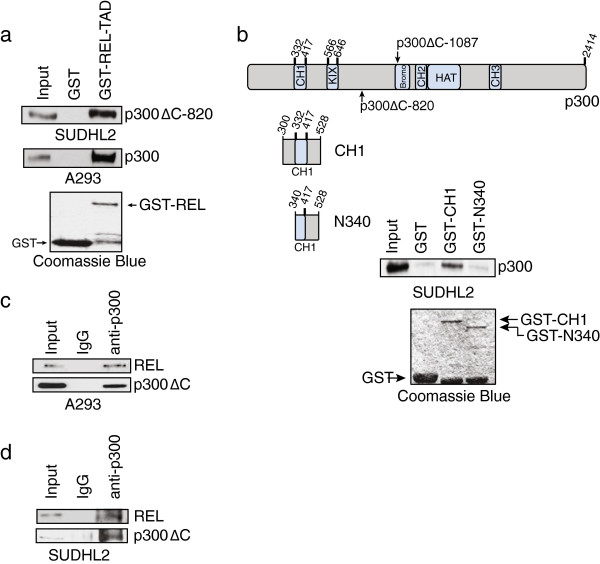
Figure 3.
p300ΔC-820 interacts with REL in vitro and in vivo. (a) A GST-REL-TAD (aa 324-587) pulldown was performed on whole-cell extracts from SUDHL2 (p300ΔC-820, top panel) or A293 cells (wild-type 300, middle panel). Bound proteins were subjected to anti-p300 Western blotting to detect p300ΔC-820 or WT p300, as indicated. (b) GST-p300 pulldown of endogenous REL from SUDHL2 whole-cell extracts. Bound proteins were subjected to anti-REL Western blotting. The structure of wild-type p300 is shown and structures of GST-p300 mutants used are indicated. (c) Nuclear extracts of A293 cells co-transfected with p300ΔC-820 and REL were immunoprecipitated with normal rabbit IgG or anti-p300 antiserum. Immunoprecipitates were subjected to anti-REL or anti-p300 Western blotting, as indicated. One percent (3 μg) of the nuclear extract used for immunoprecipitation was included as an input for the anti-REL blot and 10% (30 μg) of the nuclear extract was used as input for the anti-p300 blot. (d) Nuclear extracts of SUDHL2 cells were immunoprecipitation with normal rabbit IgG or anti-p300 antiserum. Immunoprecipitates were subjected to anti-REL or anti-p300 Western blotting, as indicated. Ten percent (25 μg) of the nuclear extract used for immunoprecipitate was included as an input for the anti-REL blot and 30% (75 μg) of the nuclear extract was used as input for the anti-p300 blot. Coomassie Blue staining was performed on 5% of GST or GST-fusion protein used in the pulldowns (a, b lower panels).