Fig. 1.
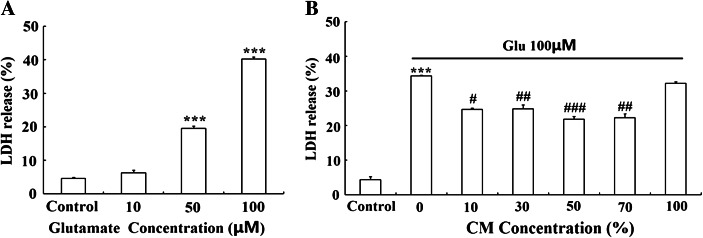
Glutamate was toxic to cultured cortical neurons and AMSC-CM reduced glutamate-induced neuronal damage in a concentration-dependent manner. a Cortical neurons at DIV9 were exposed to glutamate (10–100 μM) supplemented with 10 μM glycine for 15 min and the original culture medium was replaced. Cell damage was determined by LDH release after 18 h. Glutamate induced a dose-dependent neuronal damage. 100 μM glutamate supplemented with 10 μM glycine was chosen for all subsequent experiments. b Different concentrations of CM were added to damaged neurons following glutamate exposure and cell damage was evaluated by LDH release after 18 h. Note that glutamate-induced neuron injury was attenuated most effectively by 50 % CM, whereas 100 % CM did not mediate any neuroprotective effects. As the optimal concentration of CM, 50 % CM was used for all subsequent experiments. Data are presented as mean±SD. *** P < 0.001 versus control group, # P < 0.05, ## P < 0.01, ### P < 0.001 versus glutamate treated group. One-Way ANOVA