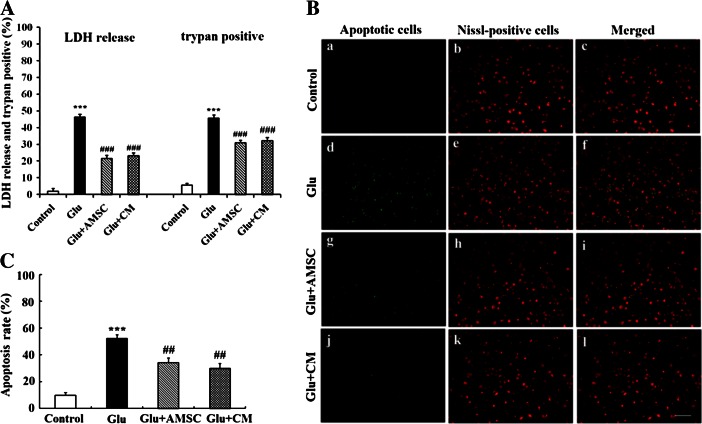
Fig. 2.
AMSCs reduced glutamate-induced damage and apoptosis in cortical neurons. Following 15 min of glutamate treatment, neurons were co-cultured with AMSCs or medium was replaced with AMSC-CM. Cell damages and apoptosis were determined by LDH release, trypan blue dye and TUNEL staining after 18 h. a Quantitative analysis of trypan blue dye and the result of LDH release. b Representative photomicrographs of total neurons stained with Nissl (red) and apoptotic nuclei stained with TUNEL (green) and merged photos were shown. (a–c) untreated control group; (d–f) neurons treated with glutamate alone; (g–i) damaged neurons co-cultured with AMSCs; (j–l) glutamate-treated neurons in the presence of AMSC-CM. c Quantitative analyses of Nissl and TUNEL co-staining. Data are presented as mean±SD. *** P < 0.001 versus control group, # P < 0.05, ## P < 0.01, ### P < 0.001 versus glutamate treated group. One-Way ANOVA. Scar bar 200 μm