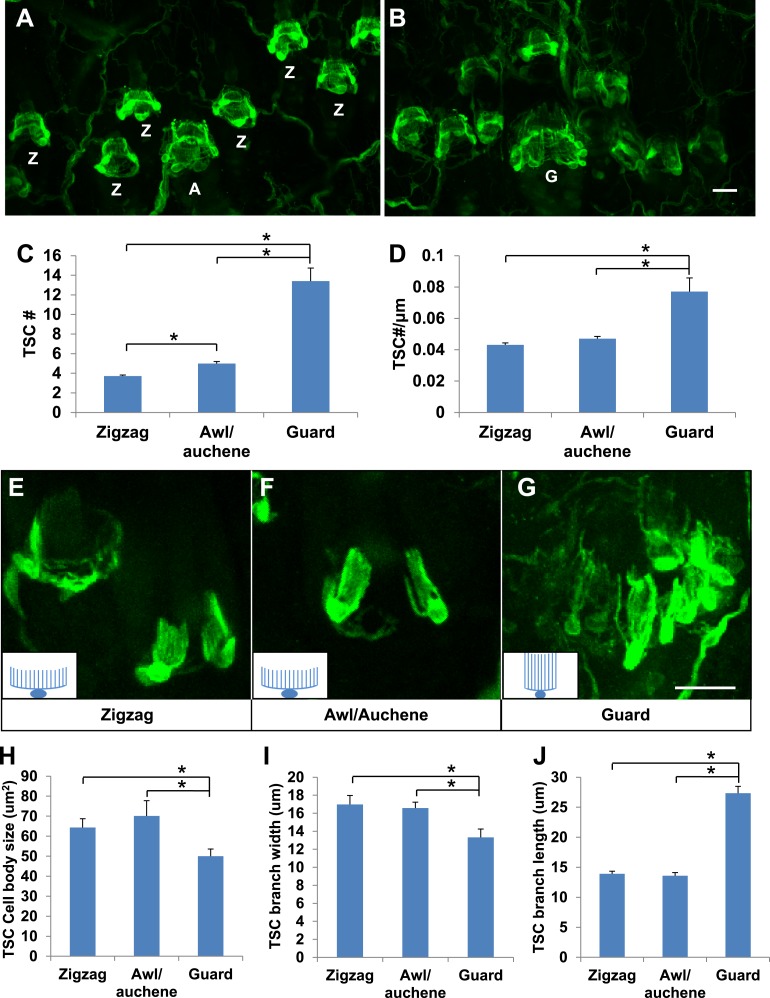
Figure 2. Guard, awl/auchene, and zigzag hair follicles have different numbers and morphologies of TSCs.
(A and B) Whole-mount immunostaining of back hairy skin using anti-S100 shows that awl/auchene (A) and zigzag (Z) hair follicles (in panel A) and guard (G) hair follicles (in panel B) have different numbers of TSCs. Scale bar, 20 μm. (C) Comparisons of numbers of TSCs at individual hair follicles. Awl/auchene hairs (5.0 ± 0.2 TSCs, n = 24 hair follicles) have slightly more TSCs than zigzag hairs (3.7 ± 0.1 TSCs, n = 64 hair follicles) (p<0.001). Guard hairs (13.4 ± 1.3 TSCs, n = 5 hair follicles) have many more TSCs than awl/auchene and zigzag hairs (p<0.001 for both comparisons). (D) Densities of TSCs at individual hair follicles were calculated by dividing the number of TSCs by the circumference of the hair follicles. Although TSC densities are comparable between zigzag (4.3 ± 0.1 TSCs/100 μm) and awl/auchene hairs (4.7 ± 0.2 TSCs/100 μm) (p=0.084), guard hair follicles (7.7 ± 0.9 TSCs/100 μm) have almost twofold higher densities of TSCs compared to zigzag and awl/auchene hair follicles (p<0.001 for both comparisons with zigzag and awl/auchene hair follicles). (E–G). In Plp1CreER;Rosa26YFP animals treated with 0.01 mg of tamoxifen, TSCs were sparsely labeled to visualize the morphologies of individual TSC associated with different hair follicle types. Insets in E–G are schematic images of TSCs to summarize the differences observed between TSCs associated with guard hairs vs awl/auchene and zigzag hairs. Scale bar, 20 μm. (H–J) Sizes of TSC cell bodies (H), widths of total processes of individual TSCs (I) and lengths of TSC processes (J) were measured at zigzag, awl/auchene, and guard hair follicles. Although all three parameters are comparable between zigzag and awl/auchene hair follicles, indicating similar morphologies, individual TSCs at guard hair follicles have significantly smaller cell sizes, and narrower and longer processes compared to the other two hair follicle types (Zigzag hair follicles: cell body size, 64.3 ± 4.5 μm2; width of processes, 17.0 ± 1.0 μm; length of processes, 13.9 ± 0.4 μm; n = 25 hair follicles. Awl/auchene: cell body size, 70.1 ± 7.6 μm2; width of processes, 16.6 ± 0.7 μm; length of processes, 13.6 ± 0.6 μm; n = 10 hair follicles. Guard hair follicles: cell body size, 50.0 ± 3.5 μm2, p<0.05 compared with zigzag or awl/auchene hairs; width of processes, 13.3 ± 0.9 μm, p<0.05 compared with zigzag or awl/auchene hairs; length of processes, 27.3 ± 1.1 μm, p<0.001 compared with zigzag or awl/auchene hairs; n = 16 hair follicles). Animals around 3 weeks of age were used in these whole-mount immunostaining experiments.