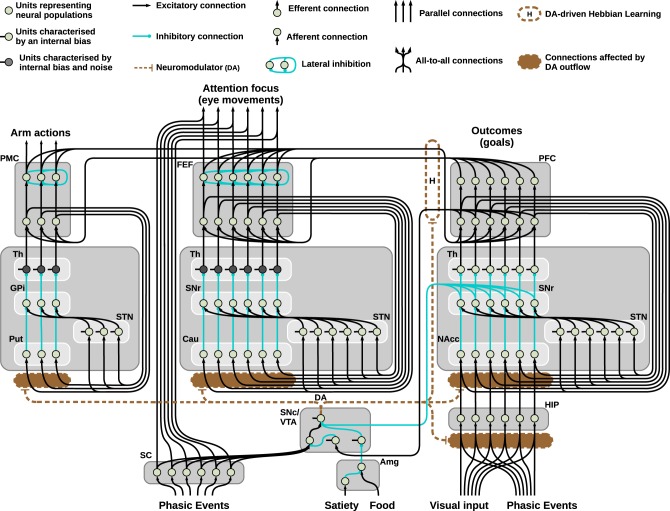
Figure 2.
Neural architecture of the model used to solve the mechatronic board task: three striatocortical loops reciprocally connected via learned cortico-cortical connections. The system allows the agent to autonomously explore the environment, perceive intrinsically motivating signals (flashes of light), learn and exploit the learned association to pursue a maximizations of rewards.