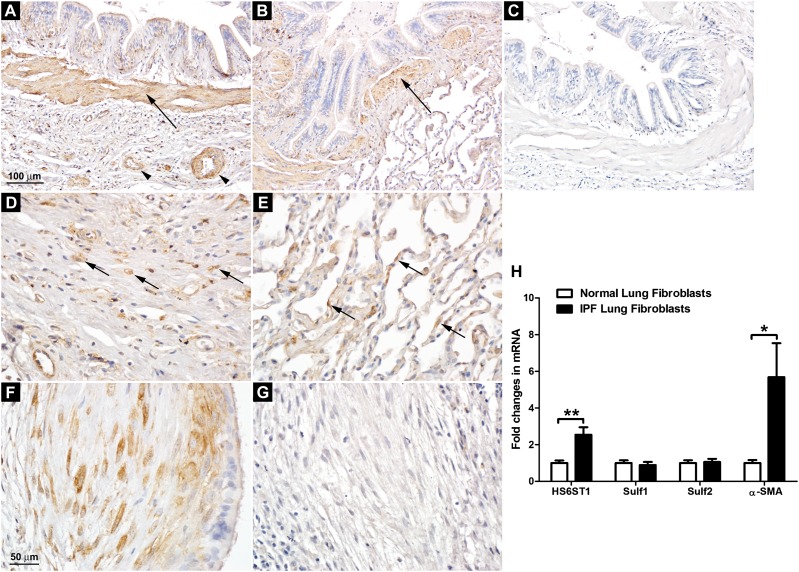
Figure 4.
Overexpression of HS6ST1 in IPF lung fibroblasts. (A) HS6ST1 immunostaining in the IPF lung. (B) HS6ST1 immunostaining in the normal lung. (C) Control staining with nonimmune mouse IgG in the IPF lung. Smooth muscle cells surrounding the bronchi (arrows in A and B) and vascular structures (arrowheads in A) in normal and IPF lungs expressed high levels of HS6ST1. (D) HS6ST1 immunostaining in the interstitium of the IPF lung. (E) HS6ST1 immunostaining in the alveoli in the normal lung. Scattered HS6ST1 positivity was observed in the distorted interstitium of the IPF lungs (arrows in D) and in the interalveolar septa of the normal lungs (arrows in E). (F) HS6ST1 immunostaining in the fibroblastic focus in the IPF lung. (G) HS6ST2 immunostaining in the fibroblastic focus in the IPF lung. A–C are at the same magnification, and D–G are at the same magnification. Images shown are representative of data from five normal and seven IPF lungs. (H) Analysis of mRNA expression of HS6ST1, Sulf1, Sulf2, and α-smooth muscle actin (SMA) in primary normal (n = 4) and IPF (n = 5) lung fibroblasts by quantitative RT-PCR. Fold changes were normalized to the expression of the housekeeping gene 36B4. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01.