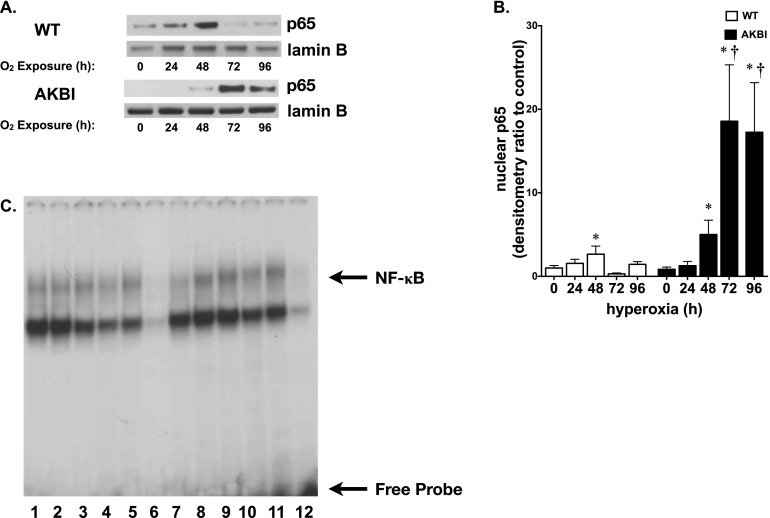
Figure 3.
Hyperoxia-induced NF-κB activation is prolonged in AKBI mice. (A) Representative Western blot showing p65 in lung nuclear extracts from WT and AKBI mice exposed to room air or hyperoxia (O2 > 95%, 24–96 hr), with Lamin B as loading control. (B) Densitometric evaluation of nuclear p65. Values are means ± SEM (n = 4/time point); *P < 0.05 versus unexposed control; †P < 0.05 versus paired WT exposure. (C) Representative electrophoretic mobility shift assay of nuclear extracts from WT and AKBI lung after exposure to room air or hyperoxia (O2 > 95%, 96 h). Bands representing NF-κB consensus sequence binding and free probe are labeled. Lane 1, WT unexposed; lanes 2–5, WT exposed to 96 hours hyperoxia; lane 6, WT cold, WT exposed to 96-hour hyperoxia plus 50-fold excess of unlabeled oligonucleotide; lane 7, AKBI unexposed; lanes 8–11, AKBI exposed to 96-hour hyperoxia; lane 12, AKBI cold, AKBI exposed to 96-hour hyperoxia plus 50-fold excess of unlabeled oligonucleotide.