Figure 6.
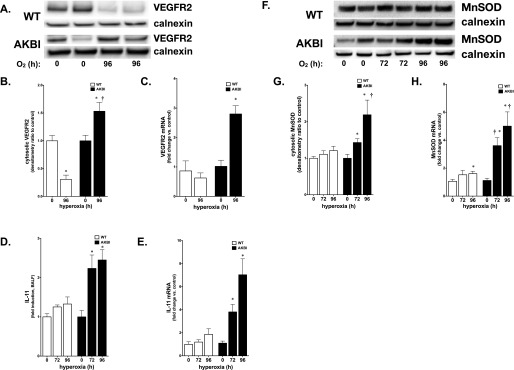
Hyperoxia induces expression of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (VEGFR) 2, IL-11 and manganese superoxide dismutase (MnSOD) in AKBI mice. (A) Representative Western blot showing VEGFR2 from whole-lung homogenate from WT and AKBI mice exposed to hyperoxia (O2 > 95%, 96 h). (B) Densitometric evaluation of VEGFR2. Values are means ± SEM (n = 4/time point); *P < 0.05 versus unexposed control; †P < 0.05 versus paired WT exposure (C) Pulmonary VEGFR mRNA expression in WT and AKBI mice exposed to room air or hyperoxia (O2 > 95%, 96 h). Values are means ± SEM (n = 4/time point); *P < 0.05 versus unexposed control and paired WT exposure. (D) IL-11 fold increase in BALF obtained from WT and AKBI mice exposed to hyperoxia assessed by ELISA (72–96 h, n = 4/time point). Data expressed as means ± SE; *P < 0.05 versus unexposed control and paired WT exposure. (E) IL-11 mRNA in WT and AKBI lung after exposure to hyperoxia (96 h, n = 4/time point). Data expressed as means ± SE; *P < 0.05 versus unexposed control and paired WT exposure. (F) Representative Western blot showing MnSOD from lung cytosolic extracts from WT and AKBI mice exposed to room air or hyperoxia (O2 > 95%, 96 h), with calnexin as a loading control. (G) Densitometric evaluation of MnSOD. Values are means ± SEM (n = 4/time point); *P < 0.05 versus unexposed control; †P < 0.05 versus paired WT exposure. (H) Pulmonary MnSOD mRNA expression in WT and AKBI mice exposed to room air or hyperoxia (O2 > 95%, 96 h). Values are means ± SEM (n = 4/time point); *P < 0.05 versus unexposed control; †P < 0.05 versus paired WT exposure.
