FIGURE 5.
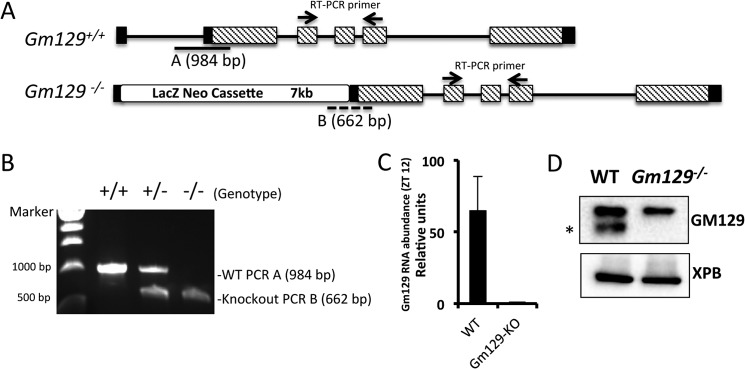
Generation of Gm129 knock-out mice. A, schematic representation of the WT (Gm129+/+) allele and targeted allele (Gm129−/−). Homologous recombination leads to the insertion of a 7-kb LacZ and Neomycin cassette between exon 1 and exon 2 in the WT Gm129 allele. Black lines represent introns. Black and dashed rectangles represent non-coding and coding exons, respectively. Solid line A and dashed line B locate the products of PCR genotyping. Two small arrows show the location of the primers used for RT-PCR (Table 1). B, primers were designed as indicated in Fig. 5A and Table 1 for genotyping. 984- and 662-bp PCR products were amplified using WT, heterozygote or knock-out mouse tail genomic DNA, respectively. C, Gm129 gene expression (normalized to Gapdh) in WT and Gm129−/− mice. The value of Gm129 expression in knock-out mice was set to 1. Error bars represent S.D. of 3 biological repeats. D, GM129 protein deficiency in Gm129−/− mouse liver. Liver nuclear extracts were prepared from wild-type (Gm129+/+) or homozygous Gm129−/− mutant mice at ZT12 and analyzed by SDS-PAGE followed by immunoblotting. The GM129 signal is marked by a black asterisk. XPB is a loading control.
