FIGURE 4.
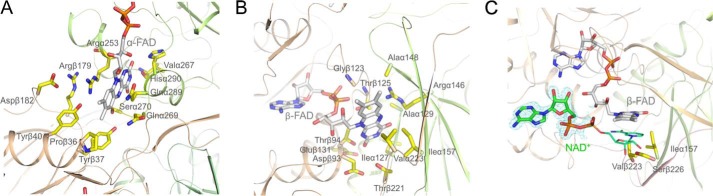
A, binding mode of α-FAD. The isoalloxazine ring is located between domains II and III. One side of α-FAD is attached along the C-terminal side of the parallel β-sheet of domain II and the opposite side is largely exposed to bulk solvent. N5 is hydrogen-bonded to Ser-270-OG. B, binding mode of β-FAD. The isoalloxazine ring of compressed β-FAD primarily binds to domains III and I. Arg-α146-NH2 is projected toward the bottom of the isoalloxazine ring and interacts with N5 of the isoalloxazine ring. C, binding of NAD+. The ADP part (in stick mode) of NAD+ (carbons in green) is predominantly fixed by its contacts to β-FAD. The nicotinamide-ribose part (in line mode) is disordered but can be modeled to the re-face of the isoalloxazine. Ile-α157, Val-β223, and Ser-β226 interfere with the nicotinamide-ribose in the conformation capable for hydride transfer and have to be displaced upon NADH binding. The electron density (in blue) is contoured at 1.5.
