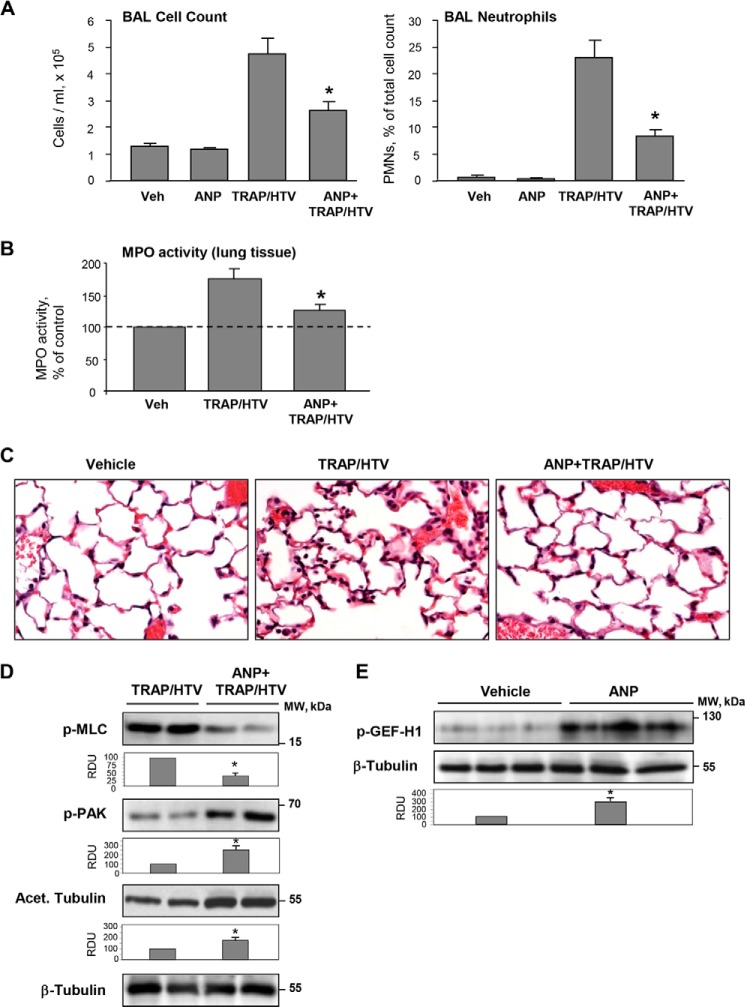
FIGURE 12.
ANP prevents lung dysfunction in the two-hit model of acute lung injury and stimulates PAK1 signaling and microtubule stability. Mice were injected with ANP or saline, followed by mechanical ventilation at HTV (30 ml/kg, 4 h) with or without TRAP6 injection or left spontaneously ventilated. A, total cell count and neutrophil counts were determined in BAL collected after TRAP/HTV exposure. *, p < 0.05 versus TRAP/HTV. B, myeloperoxidase (MPO) activity was measured in lung tissue homogenates; *, p < 0.05 versus TRAP/HTV. C, lung sections from control and TRAP6/HTV-treated mice with or without ANP. Micrographs show hematoxylin and eosin staining; magnification, ×40. D, PAK1 and MLC phosphorylation and the amount of acetylated tubulin after 4-h exposure of mice to TRAP/HTV with or without ANP were determined by Western blot analysis of lung tissue homogenates. Bar graphs depict the quantitative densitometry analysis of Western blot data. *, p < 0.05 versus TRAP/HTV. E, site-specific GEF-H1 phosphorylation in the lungs of mice treated with ANP alone was determined by Western blot analysis. Equal protein loading was confirmed by membrane reprobing for total β-tubulin; *, p < 0.05 versus saline. Error bars, S.D.