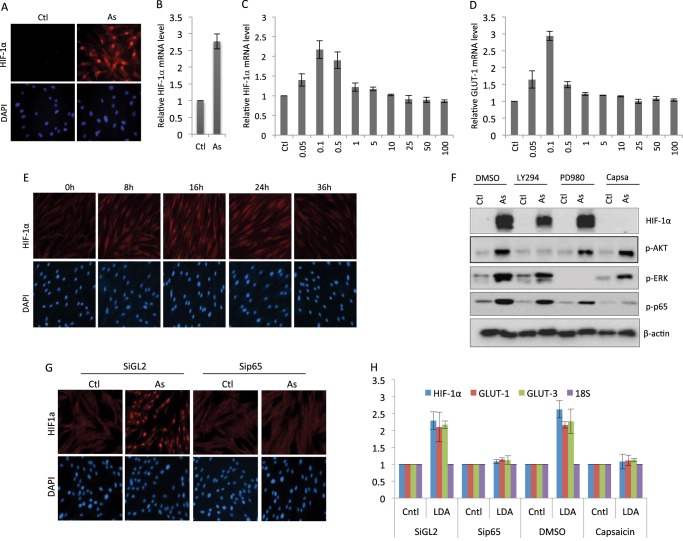
FIGURE 1.
Low doses of arsenic induce HIF-1α in an NFκB-dependent manner. Human fibroblasts were treated with sodium arsenite (As) (100 nm) for 12 h. The cells were harvested for HIF-1α immunostaining (A) or analysis of the HIF-1α transcript (B) (Ctl, control). Human fibroblasts were treated with the indicated doses of sodium arsenite. The cells were harvested 12 h later and analyzed for the levels of HIF-1α transcript (C) or GLUT-1 transcript (D). Data are mean ± S.D. from three independent experiments. F, human fibroblasts were pretreated with dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO), LY294002 (25 μm) (LY294), PD98049 (25 μm) (PD980), or capsaicin (3 μm) (Capsa) for 1 h. The cells were then treated with either solvent or 100 nm arsenic and harvested 12 h later for Western blot analysis using the indicated antibodies. G, human fibroblasts were transfected with either control RNAi (siGL2) or sip65. The cells were subjected to treatment with arsenic (100 nm) 48 h post-transfection. The cells were harvested 12 h later for HIF-1α immunostaining. H, human fibroblasts were transfected with either control RNAi or sip65 for 48 h or pretreated with dimethyl sulfoxide or capsaicin (3 μm) for 1 h. The cells were treated with either solvent (Cntl) or 100 nm arsenic (low dose arsenic, LDA). The cells were harvested 12 h later and analyzed for the levels of HIF-1α, GLUT-1, or GLUT-3 transcript. Data are mean ± S.D. from three independent experiments. E, human fibroblasts were treated with sodium arsenite for the indicated time periods, and the cells were immunostained for HIF-1α.