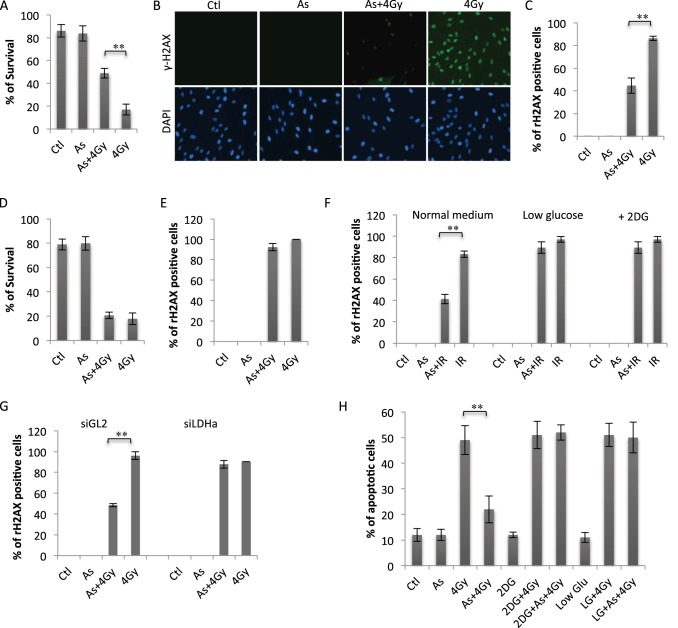
FIGURE 3.
Low-dose arsenic induces radiation resistance via induction of HIF-1α-dependent glycolysis. A, human fibroblasts were pretreated with or without arsenic (As) (100 nm) for 12 h, followed by 4-Gy irradiation. The cells were also subjected to colony survival assays. Data are mean ± S.D. from three independent experiments. **, p < 0.01. Ctl, control. B, fibroblasts were treated as indicated. The cells were harvested 1 h after irradiation and subjected to γH2AX immunostaining. C, quantification of γH2AX-positive cells shown in B. Error bars represent mean ± S.D. of three independent experiments (∼100 cells/sample). **, p < 0.01. D, human fibroblasts were transfected with either control RNAi (siGL2) or siHIF-1α. 48 h post-transfection, the cells were pretreated with arsenic (100 nm) for 12 h and then irradiated at 4 Gy. The cells were analyzed via colony survival assay. Data are mean ± S.D. from three independent experiments. E, siGL2 or siHIF-1α-expressing cells were pretreated with arsenic (100 nm), followed by 4-Gy irradiation as in E. The cells were analyzed for γH2AX 1 h after IR treatment. The numbers of γH2AX-positive cells are presented as mean ± S.D. of three independent experiments (∼100 cells/sample). **, p < 0.01. F, human fibroblasts cultured in normal medium or low-glucose (2 mm) medium were pretreated with arsenic (100 nm) or left untreated, followed after 12 h by 0- or 4.0-Gy treatment. Fibroblasts cultured in normal medium were treated with 2-DG (5 mm) 2 h before 4-Gy treatment. The cells were fixed 1 h post-4-Gy treatment and analyzed as in E. G, siGL2- or siLDH-A-expressing cells were treated and analyzed as in E. H, human lymphocytes were treated as in F and analyzed for the percentage of apoptosis. Bars represent mean ± S.D. of three independent experiments, **, p < 0.01.