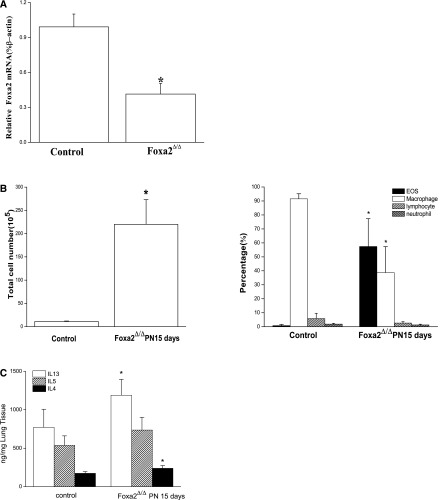
Figure 1.
Deletion of Foxa2 in respiratory epithelium caused pulmonary eosinophilic inflammation on Postnatal Day (PN) 15. (A) Loss of Foxa2 expression was confirmed by RT-PCR analysis. Foxa2 mRNA was significantly decreased. (B) Numbers of total cells and eosinophils (EOS) in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) were increased in Foxa2Δ/Δ mice on PN15. Eosinophils in BALF were increased, as assessed by Diff-Quik (Polysciences, Warrington, PA) staining. (C) Th2 cytokines (IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13) were increased in the lung tissue of Foxa2Δ/Δ mice, as determined by ELISA. The graphs represent means ± SEs (n = 5 for each genotype). *P < 0.05 versus control values, using the Student t test.