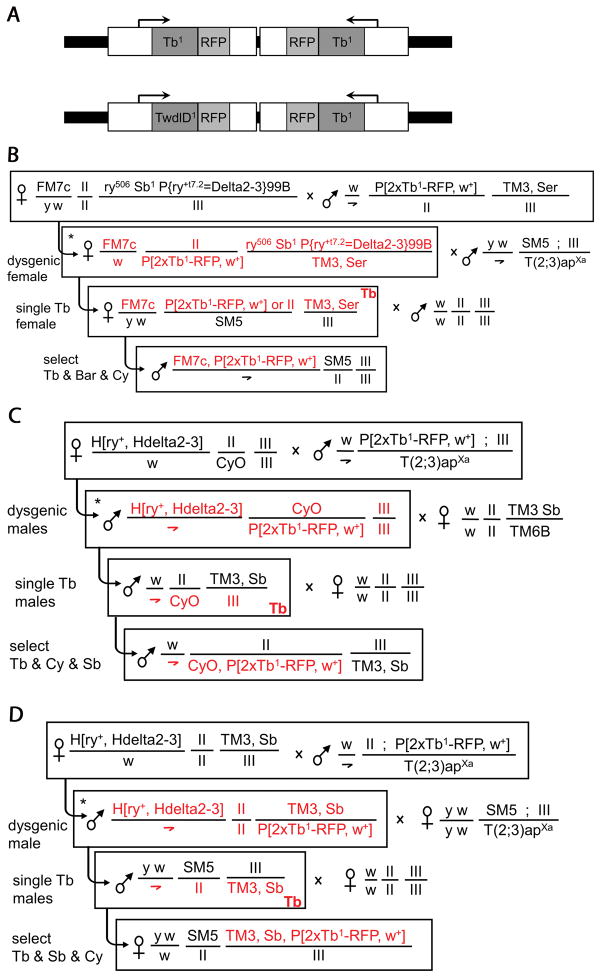
Figure 1. Constructs and genetic crosses.
A) Top: the P[2xTb1-RFP] construct contains two copies of the Tb1-RFP fusion gene previously described in Guan et al., 2006. Bottom: the P[TwdlD1-RFP, Tb1-RFP] construct contains one copy of the TwdlD1-RFP fusion gene and one copy of the Tb1-RFP previously described in Guan et al., 2006. Shaded boxes show coding regions, open boxes regulatory DNA and 5′/3′ UTRs (see Methods for details). B-D) Outline of genetic crosses for P-element transposition onto non-Tb balancer chromosomes, FM7c (B), CyO (C), TM3 (D). The asterisk denotes the dysgenic male or female; any of the chromosomes present in the dysgenic fly can acquire a new P-element insertion and are marked in red in the descendents; roman numerals indicate the corresponding unmarked chromosome.