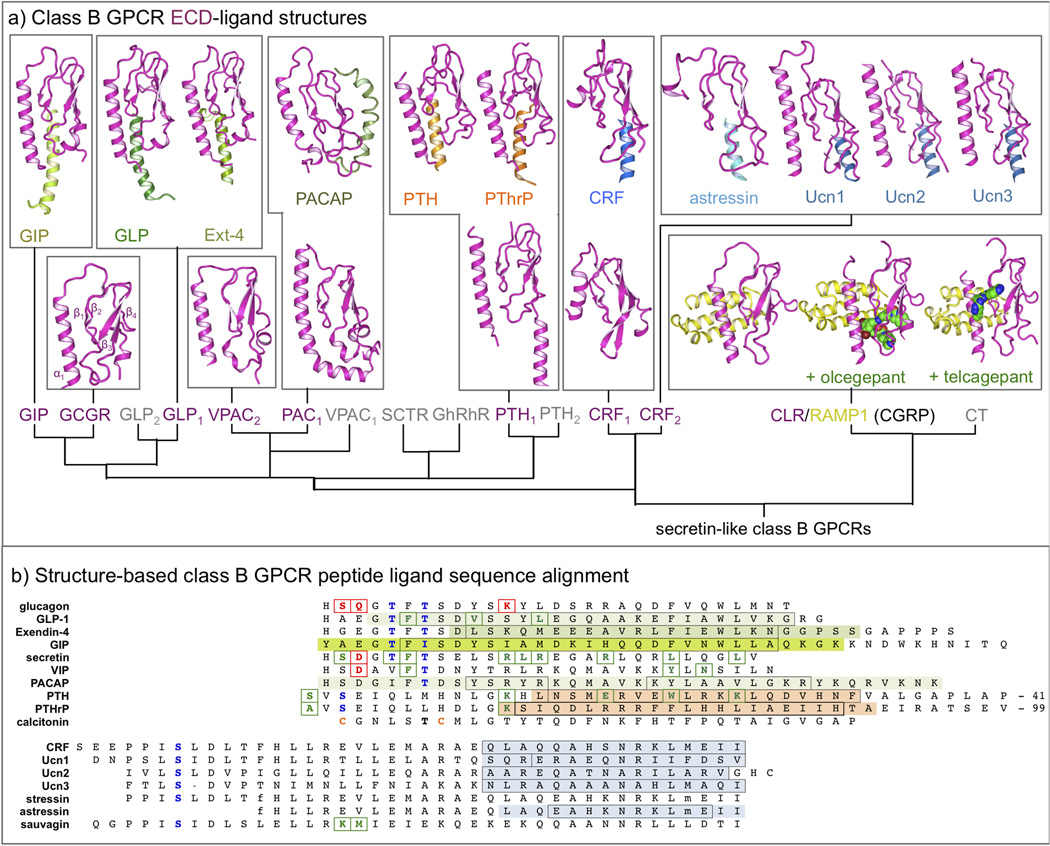
Figure 2.
(a) Overview of NMR and crystal structures of class B GPCR ECDs (magenta) and their complexes with peptide ligands (different colors) [18,19,24,34,39,51,61–68]. A complete overview of corresponding PDB IDs is presented in Table 1. (b) Structure-based sequence alignment of representative peptide ligands of class B GPCR, adopted from Parthier et al. [6]. The residues of the peptide ligands solved in ECD-ligand complex crystal structures [18,19,24,34,39,51,61–68] are marked using the same color as in Figure 2. The residues that are boxed black are found in an alpha helical conformation in the complex. Peptide ligand residues that covalently bind receptors in photo cross-linking or cysteine trapping studies [22,25,47,50,54,69,70] are colored and boxed green, while peptide ligand residues that have been mutated and studied in combination with receptor mutants [29,30,45,46,48] are colored and boxed red. Note that the first residue of GLP-1 is His7. A complete overview of all ECD structures and important peptide ligands for all class B GPCRs is presented in Table 1. Putative helix-capping residues [6] are colored blue and cysteines involved in a disulfide-bridge (calcitonin) are colored orange. D-phenylalanine (f), and norleucine (m) residues are indicated in stressin and asstressin. The last 41 and 99 residues of PTH and PTHrP, respectively, are not displayed.