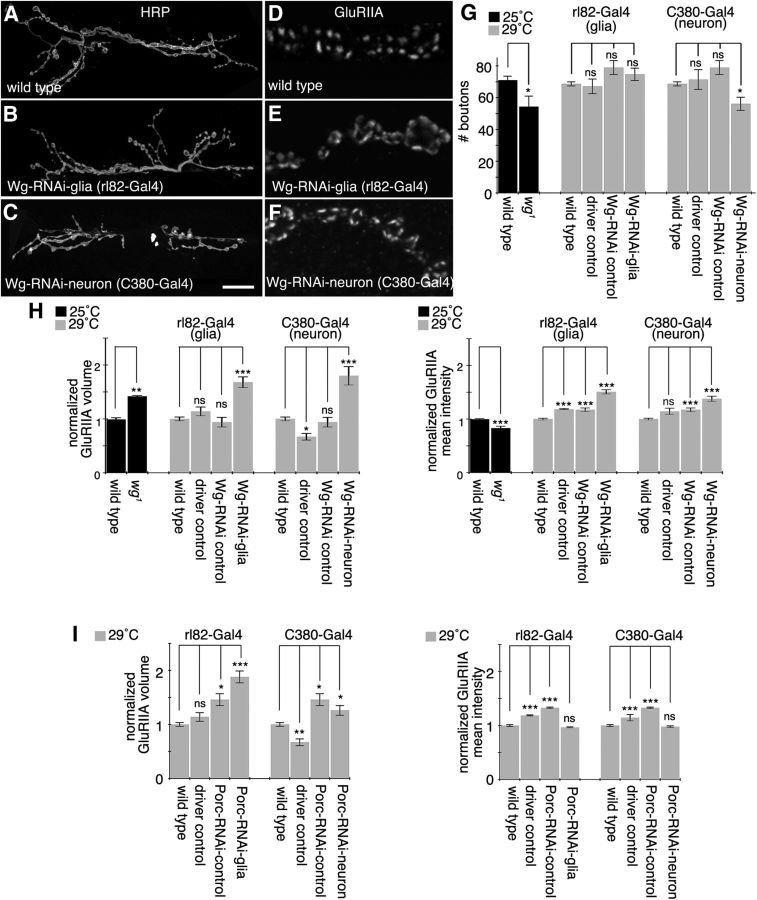
Figure 5.
SPG- and motor neuron-derived Wg regulate glutamate receptors. A–C, Confocal images of third instar larval NMJ arbors labeled with anti-HRP in wild type (A), upon expressing Wg-RNAi in SPGs (B), and upon expressing Wg-RNAi in neurons (C). D–F, Confocal images of third instar NMJ branches in preparations double labeled with anti-GluRIIA in wild type (D), upon expressing Wg-RNAi in SPGs (E), and upon expressing Wg-RNAi in motor neurons (F). G, Quantification of total bouton number for each of the indicated genotypes. H, I, Quantifications of GluRIIA volume divided by bouton volume and mean GluRIIA signal intensity in each of the indicated genotypes normalized to wild type. Gray and black bars indicate experiments performed at 29 and 25°C respectively. Error bars represent SEM. *p ≤ 0.05; **p ≤ 0.01; ***p < 0.001. Scale bar: (in C) A–C, 20 μm; D–F, 4 μm. The numbers of animals quantified for total bouton number are as follows: 25°C, wild type, 42; wg1, 13; 29°C, wild type, 166; rl82-Gal4/+ (driver control), 15; UAS-Wg-RNAi/+ (Wg-RNAi control), 9; rl82-Gal4>Wg-RNAi (Wg-RNAi-glia), 27; C380-Gal4/+ (driver control), 13; and C380-Gal4>Wg-RNAi (Wg-RNAi-neuron), 29. The numbers of arbors quantified for GluRIIA parameters are as follows: 25°C, wild type, 10; wg1, 10; 29°C, wild type, 32; rl82 driver control, 10; Wg-RNAi control, 10; Wg-RNAi-glia, 18; C380 driver control, 10; Wg-RNAi-neuron, 10; UAS-Porc-RNAi/+ (Porc-RNAi control), 10; rl82-Gal4>Porc-RNAi (Porc-RNAi-glia), 10; and C380-Gal4>Porc-RNAi (Porc-RNAi-neuron), 10.