Figure 3.
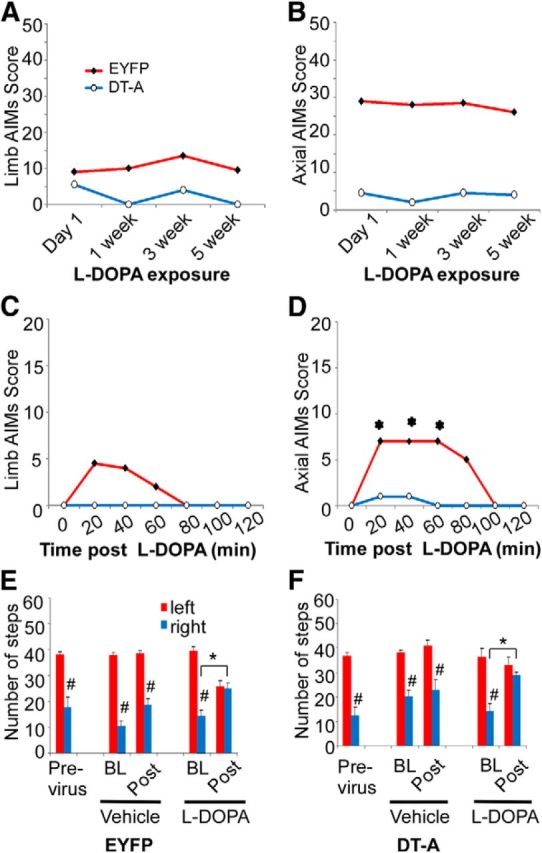
Effect of striatal cholinergic neuron ablation of l-DOPA-induced behaviors. Hemiparkinsonian ChAT-Cre mice injected with AAV-EYFP or AAV-DT-A into lesioned striatum were treated repeatedly with l-DOPA to induce AIMS. Mice were challenged with 3 mg/kg l-DOPA at the indicated time points and total limb (A) and axial (B) AIM scores were summed over a 2 h period following drug injection. C, D, The time course of limb and axial AIM during the 2 h period after l-DOPA at week 5 with chronic l-DOPA treatment. AAV-DT-A significantly reduced the overall limb and axial dyskinesia (A, B). l-DOPA did not induce dyskinesia in week 5 in mice with AAV-DT-A (C, D). The dyskinesia data represent the median (n = 6 mice for AAV-DT-A; n = 11–12 mice for AAV-EYFP). A–D, The limb and axial dyskinesia between AAV-EYFP and AAV-DT-A groups were overall statistically significant by Friedmans test (p < 0.05). *Significant difference versus baseline of the group after Wilcoxon post hoc test with Bonferroni adjustment (p < 0.00278). Motor performance was evaluated in lesioned mice using the forepaw adjusted stepping test before, and then 9–12 weeks following injection of AAV-EYFP (C) or AAV-DT-A (D). Postviral transduction, mice were tested before (BL) and 1 h after (Post) administration of vehicle (12.5 mg/kg benserazide) or l-DOPA (3 mg/kg). The stepping data represent the mean + SEM (n = 6 mice for AAV-DT-A; n = 11–12 mice for AAV-EYFP). E, F, *p < 0.05 versus baseline before l-DOPA challenge, #p < 0.05 versus corresponding left paw steps, analyzed with two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey post hoc test based on the significant interaction between sides (left vs right) × time (BL vs Post) in vehicle or chronic l-DOPA-treated groups.
