Figure 1.
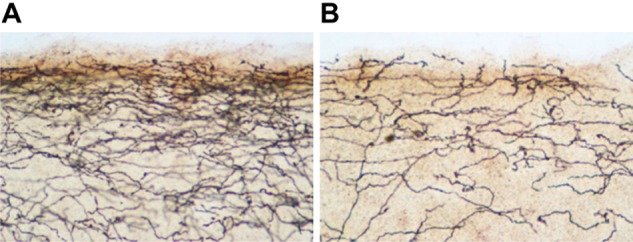
Photomicrograph of serotonin transporter-immunoreactive axons in the upper layers of occipital cortex of a control rat (A) compared to a 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA)-treated rat (B).
Notes: The animals received twice-daily injections of either saline or MDMA (10 mg/kg per injection) from the first to the fourth day of life and then were killed at 9 months of age (see Meyer et al80 for experimental details). These results illustrate the long-lasting nature of MDMA-induced serotonergic deficits when the drug is administered early in development.
