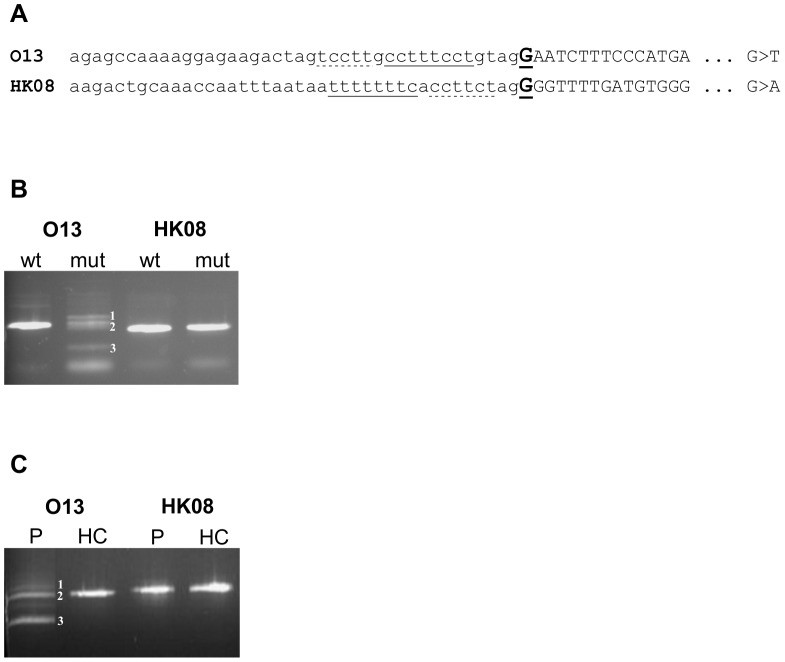
Figure 1. Analysis of the two E+1 mutations of the BTK gene, O13 (c.1482G>T) and HK08 (c.1883G>A).
(A) Schematic sequences of mutated acceptor splice sites. Introns are shown in lower-case, and exons are shown in capital letters. Mutated nucleotides are bold and underlined. The PPS are singly underlined and other polypyrimidine stretches are dashed underlined. (B) RT-PCR of minigenes transfected into HeLa cells. cDNA bands originating from O13 mutated minigene are numbered as follows: 1) cryptic 3′ss utilization 81 nt upstream of the authentic splice site (the aberrant exon starts at c.1350-81G), 2) normally spliced RNA, 3) skipping of mutated exon. (C) RT-PCR from RNA extracted from patients’ blood. P = patient’s sample, HC = healthy control sample. The O13 cDNA bands are numbered as in (B).