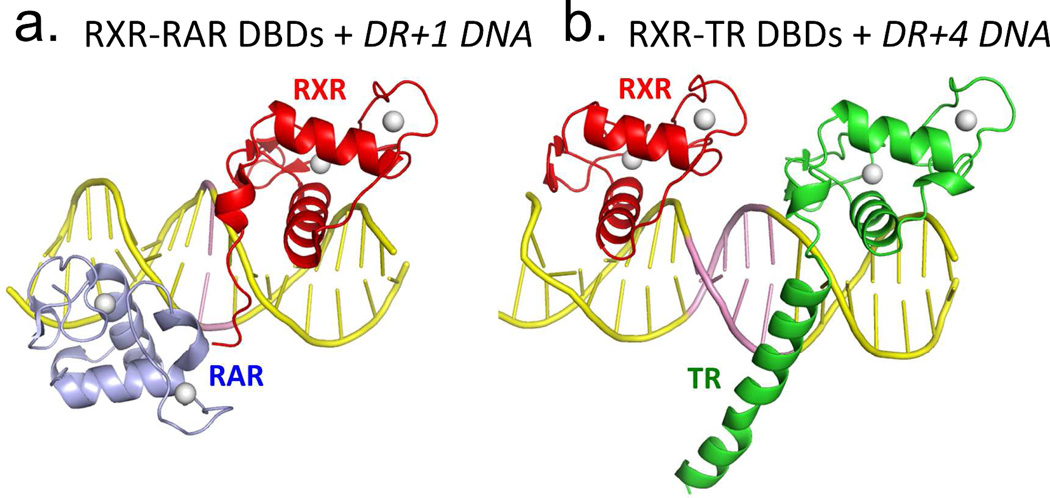
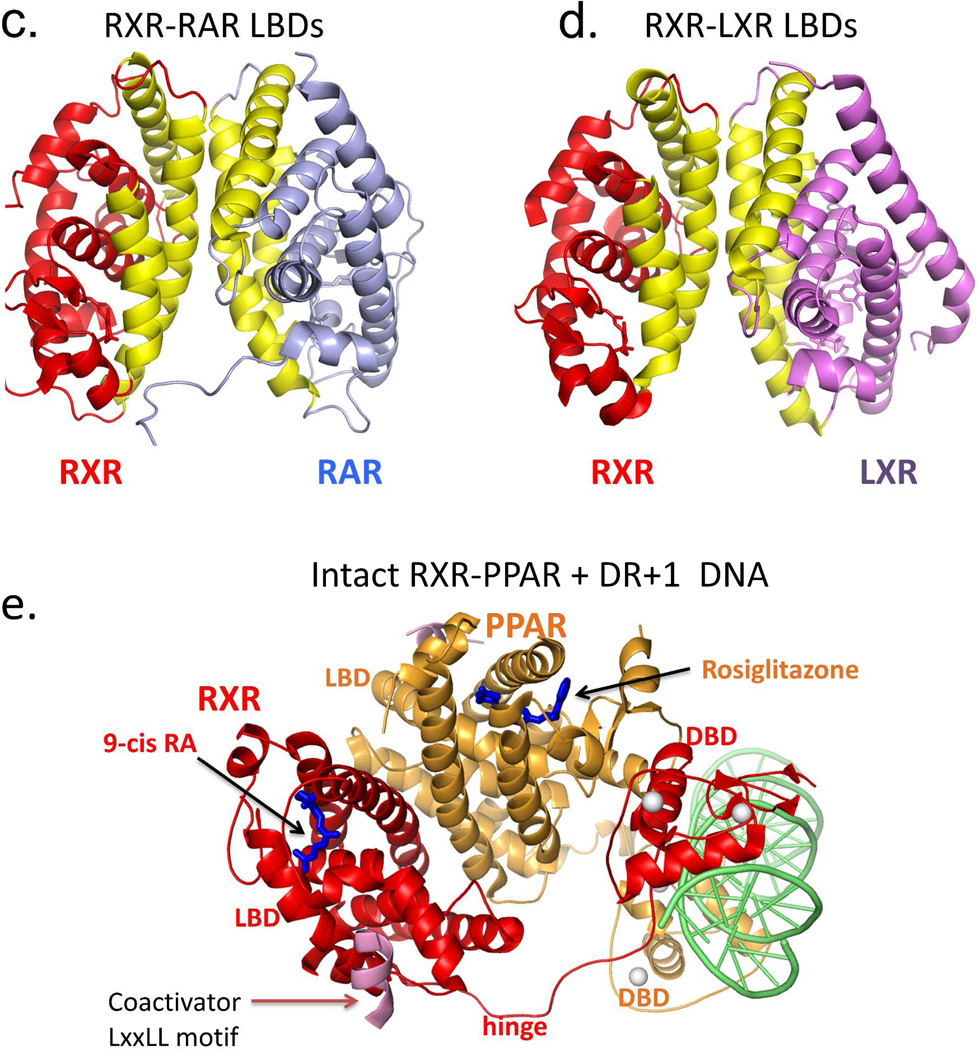
Figure 5.
RXR heterodimerization and DNA binding. (A-B) The interactions of RXR DBD and its partners (RAR or TR) on direct-repeat DNA response elements. RXR-RAR DBDs are shown on DR1 DNA, and RXR-TR DBDs are shown on DR4 DNA. Note that RXR occupies the upstream half-site in its complex with RAR, and the downstream half-site in its complex with TR. The RXR-RAR DBD complex is from PDB ID 1DSZ, and the RXR-PPAR DBD complex is from PDB ID 2NLL. B: The dimer interfaces that form between RXR LBD and other NR LBDs. Shown are the RXR-RAR (PDB ID 1XDK) and RXRLXR interfaces (PDB ID 3FAL). The regions in yellow indicate the protein-protein interfaces in these heterodimers. E. Structure of the intact RXRα-PPARγ complex on DR1 DNA (PDB ID 3E00). RXRα and PPARγ are in red and gold, respectively, with the DNA in green. The domains, ligand and coactivator peptide of RXR are labeled. In addition to the dimerization interfaces shown above, this complex also shows domain interactions involving the PPAR LBD and the RXR DBD.64