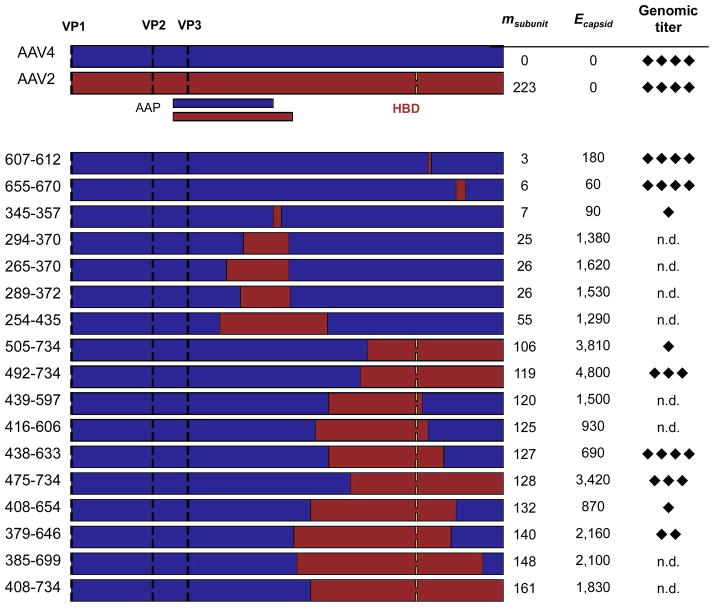
Figure 3. SCHEMA values and genome packaging properties of AAV2-AAV4 capsid chimeras.
AAV2 (red) and AAV4 (blue) genes were recombined to create capsid proteins with a range of sequence properties. Translation initiation sites (black dashes) are shown for each VP protein (VP1, VP2, and VP3), as well as the location of the AAV2 heparin-binding domain (HBD, yellow dashes) that is not present in AAV4. Locations of AAV4 and AAV2 assembly-activating proteins (AAP) are indicated under the AAV2 sequence. The effective level of mutation per chimeric subunit (msubunit) is the minimum number of amino acid mutations required to convert each chimera into AAV4, and Ecapsid represents the number of per capsid residue-residue contacts disrupted by recombination. The genomic titers of each chimera were measured by Q-PCR and scored on a scale of 1 to 4 (diamonds) relative to the detection limit and the titers obtained with AAV2 and AAV4. Each diamond represents approximately 1-log in titer. n.d. = not detected above background.