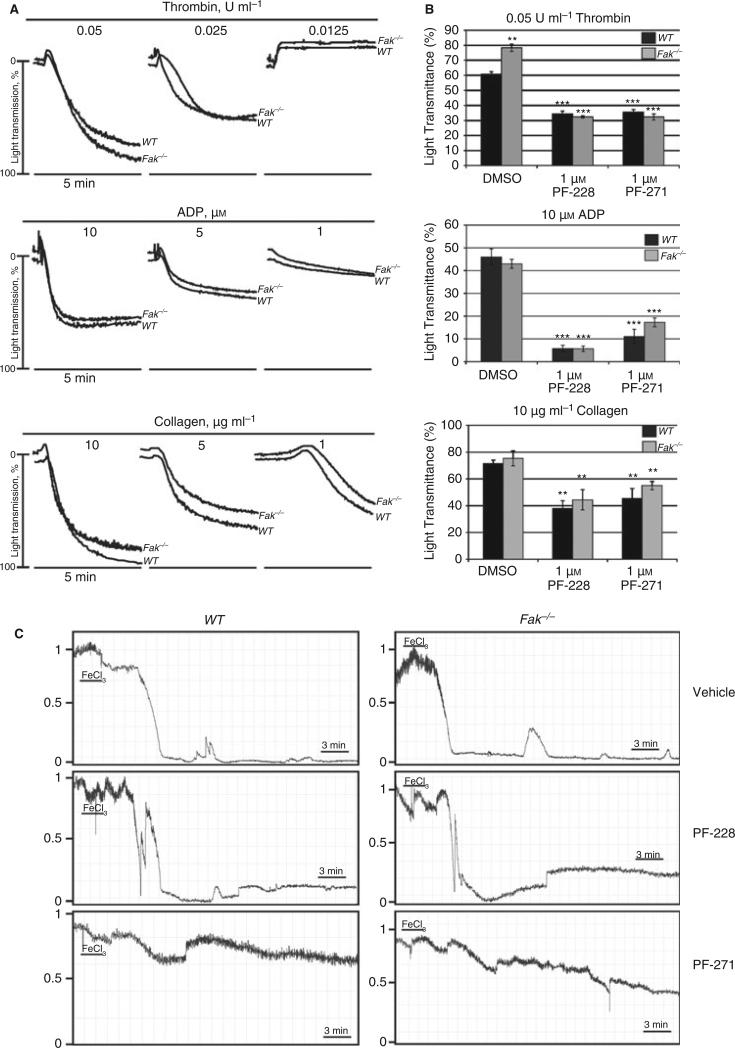
Fig. 1.
Effects of Fak ablation and FAK inhibitors on platelet function and thrombosis. Animal procedures were performed in accordance to protocols approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee, Stony Brook University. (A) Platelet aggregation was determined using washed platelets stimulated with decreasing concentrations of thrombin, adenosine 5′diphosphate (ADP), and collagen. Data are representative of at least three separate experiments. (B) Platelet aggregation was determined in the absence and presence of FAK inhibitors in WT and Fak−/− platelets following stimulation with maximal concentrations of thrombin, ADP, and collagen. Data is representative of the SEM of three independent experiments (**P < 0.01; ***P < 0.005). (C) Carotid artery occlusion assays were used to determine the effects of FAK inhibitors on in vivo thrombosis. Mice were treated with vehicle or PF-228 or PF-271 (50 mg/kg−1) for 30 min before occlusion assay. Data are representative of four mice per group.