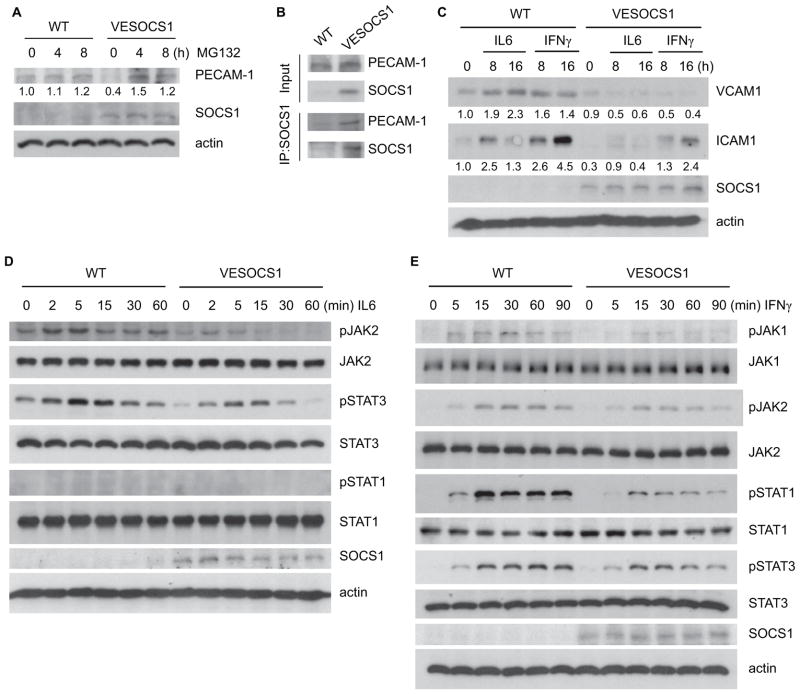
Fig. 5. EC-specific expression of SOCS1 weakens pro-inflammatory cytokine responses in primary cultured aortic EC.
(A) SOCS1 promotes proteasomal degradation of PECAM-1. Primary cultured WT and VESOCS1 mouse aortic ECs were treated with the pan-proteasome inhibitor MG132 for the indicated times. Expression of PECAM-1 and SOCS1 was determined by Western blot with the respective antibodies. PECAM-1 expression was quantified with untreated WT normalized as a value of 1.0. (B) SOCS1 associates with PECAM-1 in mouse aortic EC. Primary cultured WT and VESOCS1 mouse aortic ECs were lysed in RIPA buffer. Association of SOCS1 with PECAM-1 was determined by a co-immunoprecipitation assay with anti-SOCS1 followed by Western blot with anti-PECAM-1 or anti-SOCS1. (C) Isolated WT and VESOCS1 mouse aortic ECs were cultured in serum-free medium for 24 hours, followed by treatment with mouse IFNγ (10 ng/mL) or IL-6 (10 ng/mL) for the indicated times. Induction of endothelial adhesion molecules was determined. VCAM-1 and ICAM-1 expression was quantified with untreated WT normalized as a value of 1.0. (D–E) Isolated WT and VESOCS1 mouse aortic ECs were cultured in serum-free medium for 24 hours, followed by treatment with mouse IFNγ (10 ng/mL) or IL-6 (10 ng/mL) for the indicated times. Phosphorylation of JAK1, JAK2, STAT1, and STAT3 and total proteins were determined by Western blot with the respective antibodies. SOCS1 and β-actin were also determined. All experiments in A–E were repeated 3 times.