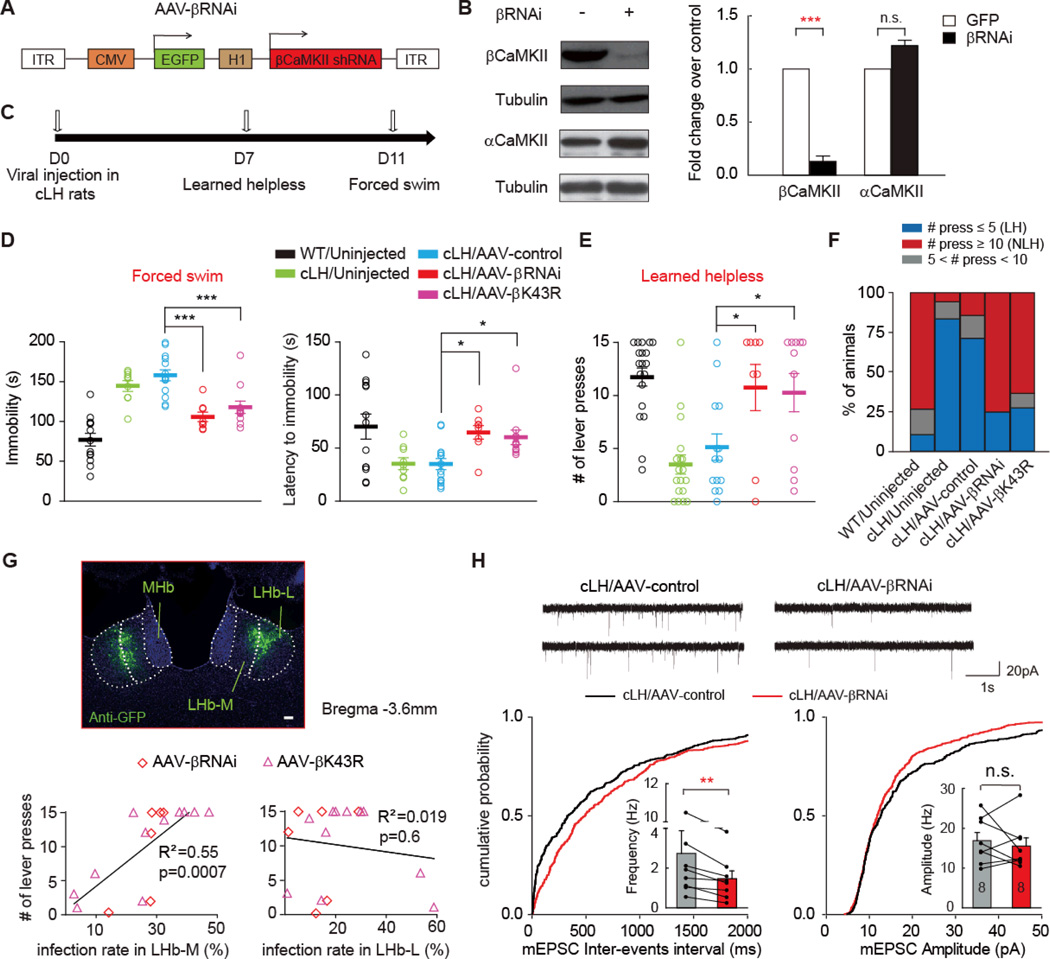
Fig. 4. Knocking-down of βCaMKII in LHb rescued depression-like phenotypes of cLH rats and reduced synaptic activity of LHb neurons.
(A) Schematics of the AAV vector engineered to overexpress an RNAi form of βCaMKII. H1: human H1 promoter. (B) Specific knocking down of βCaMKII but not αCaMKII by the βCaMKII RNAi construct. pSuper-βCaMKII-RNAi construct was co-transfected with AAV-βCaMKII or AAV-αCaMKII plasmid in 293TN cells, and expressed for 48 hrs before Western analysis. Left: representative western blot. Right: quantification of knock down efficiency. (C) Experimental paradigm for behavioral testing of cLH rats infected by virus. (D-E) Behavioral effects of expressing AAV-βRNAi and AAV-βK43R in the LHb of cLH rats in forced swim (D) or learned helpless test (EF). * p < 0.05, *** p < 0.001, one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc test. (F) Percentage of animals in each category. LH: learned helpless rats with ≤ 5 lever presses. NLH: non-learned helpless rats with ≥10 lever presses. (G) Sub-regional characterization of viral infection. Top: illustration of the division of lateral LHb (LHb-L) and medial LHb (LHb-M) in an AAV-βRNAi virus infected cLH rat brain slice. Scale bar, 100 µm. Bottom: Behavioral response in the learned helpless test plotted against infection rates in the LHb-L and LHb-M of cLH rats. (H) mEPSCs of AAV-βRNAi infected LHb neurons from cLH rats were altered. Top: example mEPSC traces. Cumulative distribution of mEPSC inter-events interval and average frequency (bottom left) or mEPSC amplitude (bottom right) of cLH LHb neurons infected by AAV-βRNAi. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001 compared with cLH/AAV-control, Wilcoxon signed-rank test.