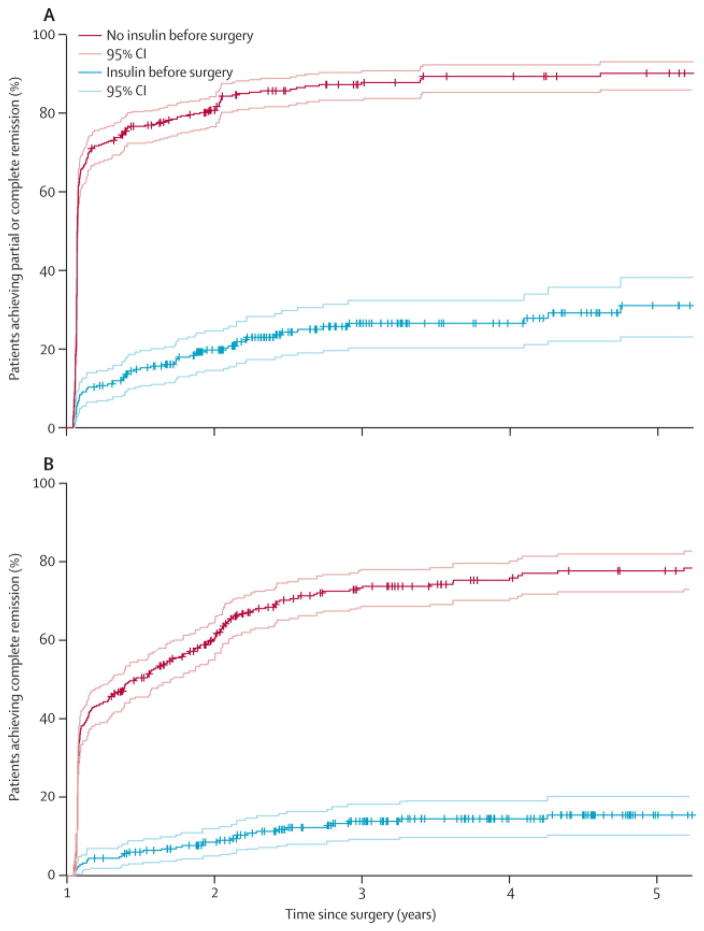
Figure 2. Kaplan-Meier survival estimates with 95% confidence intervals over five years showing the percent (%) number of patients with diabetes remission after RYGB surgery, stratified by pre-operative use of insulin.
(A) Percent remission according to the definition of “partial + complete” remission of T2D. Patients that were not using insulin preoperatively had a probability range of 70·6%-90·1% for achieving remission of T2D (early or late). T2D patients using insulin preoperatively (T2D+I), on the other hand, had a probability range of 10·3%–31·1% for achieving remission of T2D (early or rate). (B) Percent remission according to the definition of “complete” remission of T2D. Patients that were not using insulin preoperatively had a probability range of 42·4%–77·7% for achieving remission of T2D (early or late). T2D patients using insulin preoperatively (T2D+I), on the other hand, had a probability range of 4·4%–15·4% for achieving remission of T2D (early or rate). More cohort information is provided in the Supplemental information section (Tables S1–S3).