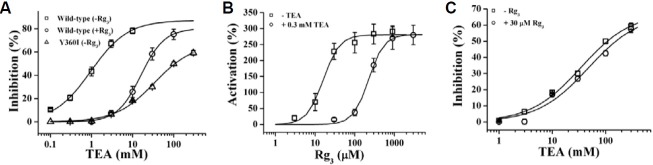
Fig. 4. Effect of TEA on Rg3 action and vice versa in wild-type channel and Y360I mutant effects on TEA and Rg3 action. (A) Concentration-response curves for TEA in the absence or presence of Rg3 (30 μM) in wild-type BKCa channels. The presence of Rg3 caused a significant rightward shift of TEAconcentration-response curves from 0.9 ± 0.1 to 20.1 ± 2.3 mM (p < 0.001, compared to the absence of Rg3). In addition, mutation of Y360 to Y360I in the absence of Rg3 shifted TEA concentration-response curve rightward from 0.9 ± 0.1 to 34.2 ± 2.6 mM (p < 0.001, compared to wild-type). (B) Concentration-response curves for Rg3 in the presence of TEA (300 μM) in wild-type BKCa channels. The presence of TEA caused a significant rightward shift of Rg3 concentration-response curves from 16.0 ± 1.8 to 224.2 ± 13.9 μM (p < 0.001, compared to the absence of TEA). (C) Effect of Rg3 on TEA concentration-response curve in Y360I mutant channel. Rg3 almost had no effect on TEA concentration-response curve in Y360I mutant channels. Data represented the mean ± S.E.M. (n = 8).