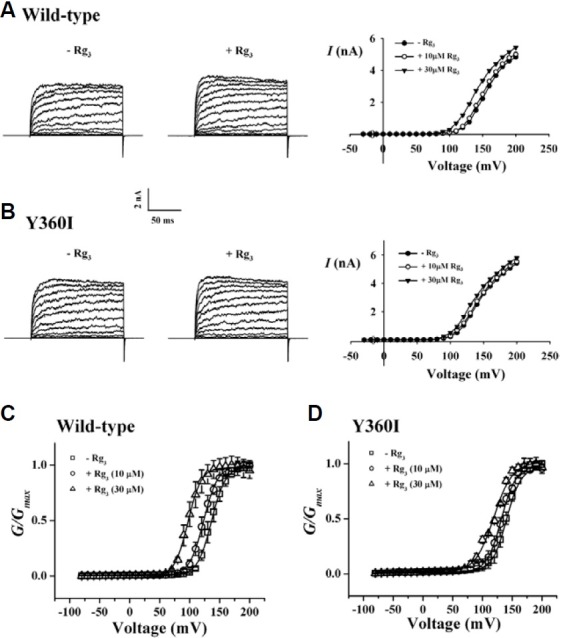
Fig. 6. Effects of Rg3 on wild-type and Y360I mutant BKCa channel currents in outside-out patch clamp configuration. (A and B) Effects of 30 μM Rg3 on the macroscopic I-V relationship of wild-type and Y360I mutant BKCa channel in the presence of 1 μM Ca2+. Representative current traces of macroscopic wild-type (A) or Y360I mutant (B) BKCa channel currents. Their respective concentrantion-dependent I-V relationships are shown in right panel for wild-type and Y360I mutant channels. Ionic currents were elicited with 200-ms step-pulses of different voltage protocols: -30 to 200 mV in 10-mV in-crements from holding potentials of -50 mV. Each data point in I-V relationships represents the mean current value measured over 198 ± 1.5 ms of test pulses. (C and D) Effects of Rg3 on the G-V relationships of wild-type (C) or Y360I mutant (D) BKCa channel currents. Conductance values were obtained from peak tail currents and normalized to the maximum conductance observed at 10 and 30 μM Rg3. V½ values were obtained by fitting independent data sets with Boltzmann function. Each symbol represents the conduc-tance values obtained from two different concentration of Rg3. Each data point represents the mean value ± S.E.M. (n = 5-6 each).