Abstract
Objective
There is evidence that natural killer (NK) cells help control persistent viral infections including hepatitis C virus (HCV). The phenotype and function of blood and intrahepatic NK cells, in steady state and after interferon (IFN) α treatment has not been fully elucidated.
Design
We performed a comparison of NK cells derived from blood and intrahepatic compartments in multiple paired samples from patients with a variety of chronic liver diseases. Furthermore, we obtained serial paired samples from an average of five time points in HCV patients treated with IFNα.
Results
Liver NK cells demonstrate a distinct activated phenotype compared to blood manifested as downregulation of the NK cell activation receptors CD16, NKG2D, and NKp30; with increased spontaneous degranulation and IFN production. In contrast, NKp46 expression was not downregulated. Indeed, NKp46-rich NK populations were the most activated, correlating closely with the severity of liver inflammation. Following initiation of IFNα treatment there was a significant increase in the proportion of intrahepatic NK cells at days 1 and 3. NKp46-rich NK populations demonstrated no reserve activation capacity with IFNα treatment and were associated with poor viral control on treatment and treatment failure.
Conclusions
NKp46 marks out pathologically activated NK cells, which may result from a loss of homeostatic control of activating receptor expression in HCV. Paradoxically these pathological NK cells do not appear to be involved in viral control in IFNα-treated individuals and, indeed, predict slower rates of viral clearance.
Keywords: CHRONIC VIRAL HEPATITIS, HEPATITIS C, IMMUNE-MEDIATED LIVER DAMAGE, IMMUNOLOGY IN HEPATOLOGY
Significance of this study.
What is already known on this subject?
NK cells form part of the innate immune response to viral infections including HCV.
There are very limited data regarding the role of intrahepatic NK cells in chronic HCV infection and during IFNα-based treatment.
NKp46 expression, a NK cell-activating receptor, has been associated with increased NK cell activity in HCV infection but in mouse models lower NKp46 expression has been associated with rapid NK cell control of viral infections.
What are the new findings?
Increased NKp46 expression is associated with increased NK cell cytotoxic activity ex vivo in HCV-infected individuals but not healthy controls.
NK cells are more activated in the intrahepatic compartment. NKp46 expression and NK cell cytotoxic activity correlates with liver inflammation. Failure of homeostatic NKp46 downregulation following NK cell activation in chronic HCV appears to drive liver pathology.
During IFNα treatment rapid viral clearance and treatment success are associated with lower pretreatment expression levels of NKp46.
How might it impact on clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
High NKp46 expression in chronic HCV infection identifies individuals most at risk of liver inflammation and at increased risk of failing IFNα-based treatment.
NKp46 provides a novel treatment target—reducing NKp46 expression may reduce inflammation in patients unsuitable for treatment and transient reduction before treatment may increase SVR rates.
Introduction
Hepatitis C virus (HCV) chronically infects 3% of the global population and represents a major global health problem. Although adaptive immune responses contribute to controlling and clearing acute HCV infection,1 2 it is clear that other branches of the immune response are important for viral control. Natural killer (NK) cells are large granular cytotoxic lymphocytes, phenotypically defined as CD3− CD56+, which play an important role in controlling viral infections. NK cells express a combination of activating and inhibitory receptors, and are functionally triggered when signalling from activating receptors overcomes that of inhibitory receptors. Activating receptors include the FcγIII receptor CD16, natural cytotoxicity receptors such as NKp30 and NKp46, and NKG2D, a C-type lectin-like receptor. There is some evidence that NK cells play a protective role in individuals exposed to HCV.3 4 However, there is no consensus between multiple studies of NK cell receptor phenotype in chronic HCV infection. Separate individual studies examining receptors such as NKp30, NKp46, and NKG2D have variously reported upregulation,5–7 downregulation8 9 or no change10 11 in HCV infection compared to healthy controls.
A similar lack of consensus emerges regarding the degree of preservation of cytotoxic function of NK cells in HCV.5 6 10 12 A recent study demonstrated that NKp46High NK cells have greater cytotoxic activity and interferon (IFN) production, allowing control of viral replication albeit using an in-vitro model.13 However, others found that NK cells retrieved from the intrahepatic compartment demonstrate a reduced cytotoxic function ex vivo.14 Key questions remain regarding how intrahepatic NK cell phenotype impinges on function, HCV pathogenesis and the successful treatment of HCV. Current treatment for HCV is based on IFNα injections. NK cells are stimulated by IFNα but the role of NK cells and their action during IFNα-based treatment is not clear. Most studies to date investigating the role of NK cells in HCV treatment have focused on peripheral blood rather than the intrahepatic compartment, but a major problem in interpreting these studies lies in not knowing whether NK cell function in blood reflects that of intrahepatic NK cells.
In this study we investigated NK cell function, using multiparameter flow cytometry, not only in matched blood and intrahepatic samples, but also by obtaining repeat serial liver biopsies (fine needle aspirations; FNA) in individuals who were being actively treated with IFNα. NK cell function was compared between individuals with HCV, other chronic liver diseases (CLD), or healthy controls. The questions we set out to address include: (1) Does chronic inflammation of the liver per se affect NK cell function? (2) Does chronic HCV infection impinge on NK cell function and phenotype in the blood and the liver? (3) Do the results obtained from blood reflect the results from liver samples? (4) Would NK cell phenotype and function predict response to treatment of HCV with IFNα?
Materials and methods
Cohort
Fifty-seven patients (35 consecutive patients with chronic HCV and 22 patients with non-viral CLD) attending University Hospital Wales were enrolled (table 1 and supplementary table, available online only). Positive anti-HCV antibodies and HCV RNA identified by reverse transcriptase PCR at two time points at least 6 months apart confirmed chronic HCV infection. Treated patients received pegylated-IFNα and ribavirin for 6–12 months depending on virus genotype. Treatment success is defined as sustained virus response (SVR) demonstrated by negative PCR tests both immediately after and at 6 months after treatment. A single consultant histopathologist assessed the biopsy samples according to Ishak necroinflammatory score (0–18) and fibrosis stage (0–6).15
Table 1.
Donor characteristics
| Characteristics | HCV | Chronic liver disease | HCV donating FNA | HCV donating PBMC for cytotoxicity experiments |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | 35 | 22 | 24 | 23 |
| Mean age (range) | 48 (27–67) | 50.6 (29–69) | 49 (27–65) | 45.7 (27–67) |
| Male:female | 25 : 10 | 12 : 10 | 17 : 7 | 15 : 8 |
| Median viral load (range) | 1.45×106 (1.9×103–3×107) | – | 1.3×106 (1.9×103–3×107) | 7.5×105 (3.1×103–3×107) |
| Median NI score (range)* | 5 (0–8) | 1 (0–6) | 5 (2–8) | 5 (0–8) |
| Median fibrosis score (range)* | 2 (0–6) | 2 (0–6) | 2 (0–2) | 2 (1–6) |
| HCV genotype | ||||
| 1 | 17 | – | 16 | 9 |
| 3 | 15 | – | 8 | 11 |
| 4 | 1 | – | – | 1 |
| 5 | 1 | – | – | 1 |
| 1&3 | 1 | – | – | 1 |
*Necroinflammatory and fibrosis scores according to Ishak criteria.
FNA, fine needle aspiration; HCV, hepatitis C virus; NI, necroinflammatory; PBMC, peripheral blood mononuclear cell.
Degranulation assays
CD107a externalisation on NK cell degranulation was used as a marker of NK cell cytotoxic activity.16 Frozen peripheral blood mononuclear cell (PBMC) samples were obtained from 23 chronic HCV patients pretreatment (see supplementary table, available online only), 13 healthy donors (HD) and 10 CLD donors. Cells were thawed, washed and cultured overnight at 106/ml in RPMI media–10% fetal bovine serum with 0, 50 or 1000 IU/ml IFNα (Roferon, Roche, UK). PBMC were washed and exposed to Huh7.5 (human hepatoma cell line) or K562 (erythroleukaemic cell line lacking in MHC class I) target cells in DMEM–10% fetal bovine serum (E:T ratio=5 : 2) with CD107a-PE (BD Biosciences, Oxford, UK) for 4 h and 1 μl of Golgi stop (BD Biosciences) for the final 3 h. Non-adherent cells were washed and stained with Aqua live/dead stain (Invitrogen, Paisley, UK) and fluorochrome labelled monoclonal antibodies specific for CD3-APCH7, CD14-APCH7, CD19-APCH7 (BD Biosciences), CD16-FITC, NKG2D-APC, NKp30-Biotin (Miltenyi Biotech, Bisley, UK), streptavidin-PECy7 (eBioscience, Hatfield, UK), CD56-PerCP.Cy5 and NKp46-PB (Biolegend, Cambridge, UK). Cells were washed, fixed with 2% paraformaldehyde solution and analysed by flow cytometry using a CyAn ADP flow cytometer (Beckman-Coulter). The data were analysed using FlowJo software (Ashland, Oregon, USA). We compared the ratio of CD107a upregulation with a strong stimulus (K562 cells plus 1000 IU/ml IFNα) to a weak stimulus (Huh7.5 cells plus 50 IU/ml IFNα), that is, functional ratio=% NK cells expressing CD107a with strong stimulus÷% NK cells expressing CD107a with a weak stimulus, as described previously17 and illustrated in supplementary figure S5 (available online only).
The expression of NK cell-activating receptor ligands on Huh7.5 and K562 cells was analysed by flow cytometry using NKp30 and NKp46–human Fc fusion proteins (R&D Systems, Abingdon, UK) and anti-human FcγPE antibody (eBioscience); and mouse monoclonal antibodies (BAMOMAB, Munich, Germany) to the NKG2D ligands (MICA, MICB and ULBP2) and anti-mouse-AF647 secondary antibody (Invitrogen).
Intrahepatic NK cell samples
Intrahepatic NK cells were sampled by FNA of the liver from 46 consecutive patients (24 HCV and 22 CLD controls) attending for pretreatment liver biopsy (table 1). Two per cent lignocaine was infiltrated, a 22 gauge spinal needle (Becton Dickinson, Madrid, Spain) was inserted and a single cell suspension aspirated into RPMI 10% foetal calf serum (FCS) with 250 μl heparin on ice. Intrahepatic samples are essentially intracapsular and due to the exceptionally vascular nature of the liver, will inevitably include lymphocytes from the small sinusoids as well as the intracellular space. However, heavily blood-stained aspirates were discarded and the needle passed into fresh liver. Paired peripheral blood samples were taken and lymphocytes were separated by lymphoprep density gradient. Samples were washed twice in phosphate-buffered saline and stained as above and in addition antibodies for CD107a-FITC (Miltenyi Biotech), and NKG2A-PE (R&D Systems). Cells were then permeabilised and fixed (Fix/Perm; eBioscience) and stained with antibodies to Granzyme B-APC (Invitrogen), Ki67-PE (Biolegend) and IFNγ-e450 (eBioscience). Cells were washed, fixed and analysed by flow cytometry as described above. Nine patients agreed to repeated FNA and peripheral blood sampling during IFNα treatment. Sampling time points were pretreatment, days 1 and 3; weeks 1, 2, 4 and 12.
Viral load analysis
HCV RNA was quantitated by reverse transcriptase PCR (detection down to 30 copies per ml), Cobas Ampliprep/Cobas Taqman HCV test (Roche Diagnostic Systems). Lab21 (Cambridge, UK) undertook this work.
Immunohistochemistry
Fixed and mounted liver biopsy specimens taken from HCV-infected patients were dewaxed and antigen retrieval performed. Endogenous peroxidase activity was suppressed with Peroxidase Suppressor (Thermo Scientific) and sections blocked with 2.5% normal horse serum (Vectorlabs). Sections were stained overnight with goat anti-NKp46 (Vector) and rabbit anti-CD3 (DakoCytomation) antibodies diluted in 1% bovine serum albumin, detected with anti-goat or anti-rabbit Immpress and visualised with 3, 3′-diaminobenzidine (DAB) (VectorLabs). Sections were counterstained with haematoxylin, dehydrated and mounted with Dpex (Panreac Life Sciences, Barcelona, Spain). Photomicrographs were taken using a Nikon microscope.
Statistical analysis
A comparison of phenotypic and functional markers was made using Student's t test assuming normal distribution of data. The kinetic parameters of viral clearance (rate constant k in day−1) were calculated from a non-linear regression curve best fit (y=y0e−kx+plateau; y0=viral concentration day 0, plateau=final viral concentration after treatment). Comparison of NK functional markers with activation markers and rate of viral clearance was by linear regression. Comparison of non-parametric data and NK markers was by Spearman's r analysis. Software employed was Excel 2011 and GraphPad Prism V.5.0.
Results
Patient demography
Thirty-five patients with chronic HCV infection and 22 CLD patients were recruited (summarised in table 1 and individual data in the supplementary table, available online only). Twenty four patients completed combined IFNα and ribavirin treatment; seven failed to clear the virus and 17 achieved SVR.
NK cell frequency, phenotype and function in the blood of patients with chronic HCV.
The frequency and phenotype of NK cells in blood samples taken from patients with chronic HCV infection, CLD and healthy controls was compared. NK cells were defined as single live cells within the lymphocyte gate, which were CD56+ yet CD3− CD14− and CD19− to exclude T cells, monocytes and B cells, respectively (see supplementary figure S1A–D, available online only). The proportion of lymphocytes that were NK cells was slightly lower in the HCV cohort (more marked for genotype 1 patients, data not shown) compared to HD (mean 10.1% vs 13.3% p=0.05; figure 1A). Perhaps surprisingly, despite the presence of chronic HCV infection, the phenotype of blood NK cells (eg, CD56Bright:Dim ratio, expression of CD16, NKp30, NKG2D and CD107a) does not differ significantly to HD (data not shown). There was a slight reduction in the percentage of NKp46+ cells in the HCV cohort compared to HD (mean 72.1% vs mean 80.6% p=0.06; figure 1B).
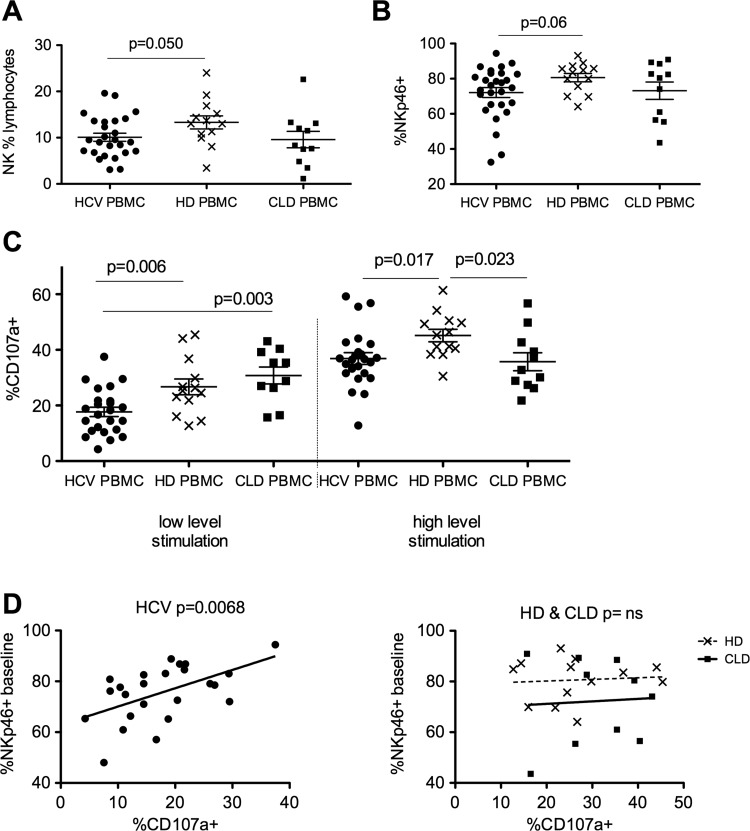
Figure 1.
Peripheral blood natural killer (NK) phenotype and function in hepatitis C virus (HCV), non-viral chronic liver disease and healthy donors (HD). (A) NK cells as a percentage of lymphocytes in the peripheral blood of HCV (10.1%) and HD (13.3% unpaired t test p=0.05) and chronic liver diseases (CLD). (B) Comparison of NKp46 expression on peripheral blood NK cells in HCV and HD (unpaired t test p=0.06) and CLD. (C) Degranulation (CD107a externalisation) is reduced in the HCV cohort compared to HD and CLD at low-level stimulation (50 IU/ml interferon (IFN)α and Huh7.5 target cells, p=0.006, unpaired t test) and HD at high-level stimulation (1000 IU/ml IFNα overnight and K562 target cells, p=0.017). (D) NK cytotoxic function correlates with baseline NKp46 expression in the HCV cohort (left panel p=0.0068, r2=0.29) but not the HD or CLD cohorts (right panel p=ns). Mean and SEM shown. PBMC, Peripheral blood mononuclear cells.
Following stimulation of NK cells with the weak stimulus (Huh7.5 cells plus 50 IU/ml IFNα), NK cell degranulation as measured by CD107a was significantly reduced in the HCV cohort compared to HD and CLD donors. Following stimulation with a stronger stimulus (K562 cells plus 1000 IU/ml IFNα) NK cell degranulation was reduced in both the HCV patients and CLD controls compared to HD (figure 1C). Intriguingly, the NK cell activation in vitro strongly correlated to the percentage NKp46+ cells in the HCV cohort (p=0.0068, r2=0.29; figure 1D, left panel panel) but not the HD or CLD donors (figure 1D, right panel). No such correlations were observed for other activating receptors (CD16, NKp30 and NKG2D; data not shown).
Expression of the ligands for NKp30, NKp46 and NKG2D on Huh7.5 and K562 targets was examined by flow cytometry. Ligands for NKp30 and NKG2D were expressed at far higher levels on K562 cells than Huh7.5 cells, in line with their superior ability to stimulate NK cells. Conversely, NKp46 ligands, although expressed at comparatively low levels, were nevertheless better expressed on the Huh7.5 cells than K562 cells (see supplementary figure S2A,B, available online only). Therefore, alterations in NKp46 expression (ie, NKp46-rich vs NKp46-low cells) is more likely to impact on killing of Huh7.5 than K562 cells, as suggested by the data shown in figure 1D (and see figure 4C).
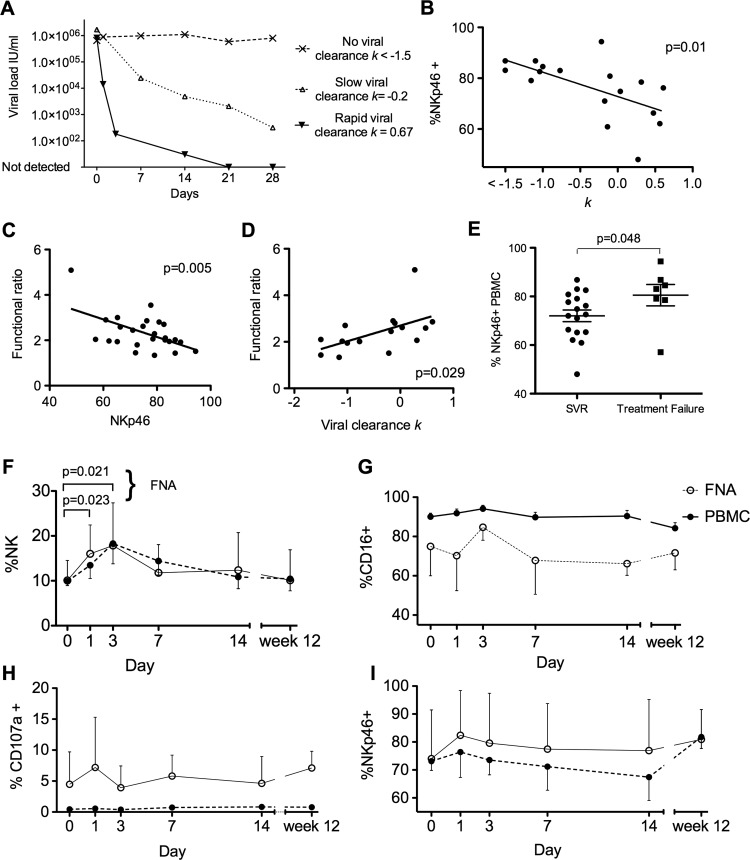
Figure 4.
Intrahepatic and peripheral blood natural killer (NK) cells during the first 12 weeks of interferon (IFN)α treatment and NKp46+ population correlates with rate of viral clearance. (A) Representative rates of viral decline: Rapid response to IFNα treatment with reduction in viral load k=0.67. Slow viral response with k=−0.2 and no response to treatment k<−1.5. (B) Percentage of peripheral blood NK cells that are NKp46+ and rate of viral decline during IFNα treatment (p=0.01, r2=0.36). (C) Functional ratio inversely correlates with percentage of NK cells that are NKp46+ (p=0.005, r2=0.29) (D). Functional ratio correlates with rate of viral clearance (p=0.029, r2=0.3). (E) Patients who clear HCV with IFNα treatment have lower expression of NKp46 at baseline than those who fail treatment (p=0.048). (F) Variations in NK cells as percentage of lymphocytes during the first 12 weeks of IFNα treatment in the peripheral blood and intrahepatic compartments (n=9). Proportion of intrahepatic NK cells increases at day 1 and day 3 (paired t test pretreatment and day 1 p=0.023 and pretreatment and day 3 p=0.021). (G) Percentage of CD16+. (H) Percentage of CD107a externalisation. (I) Percentage of NKp46+. FNA, Fine needle aspiration; PBMC, peripheral blood mononuclear cells; SVR, sustained viral response.
In summary, although the pattern of expression of markers on blood-derived NK cells is not strikingly different in HCV-infected subjects, their cytotoxic function was significantly reduced. These data also suggest NKp46 plays a particular role in the pathobiology of NK cells in HCV infection.
Intrahepatic NK cells demonstrate an activated phenotype compared to blood-derived population in patients with CLD
To assess NK cells within the intrahepatic compartment we obtained multiple samples from 24 HCV patients and 22 CLD patients. The overall frequencies of NK cells were strikingly similar between blood-derived and intrahepatic populations (figure 2A, left panel), with the frequencies between the two compartments strongly correlating (HCV infection p=0.0007, r2=0.4; CLD p=0.024, r2=0.23; figure 2A, right panel). These data suggest that the reduction in NK proportion in HCV compared to HD (figure 1A) is not related to a migration of NK cells to the inflamed liver.
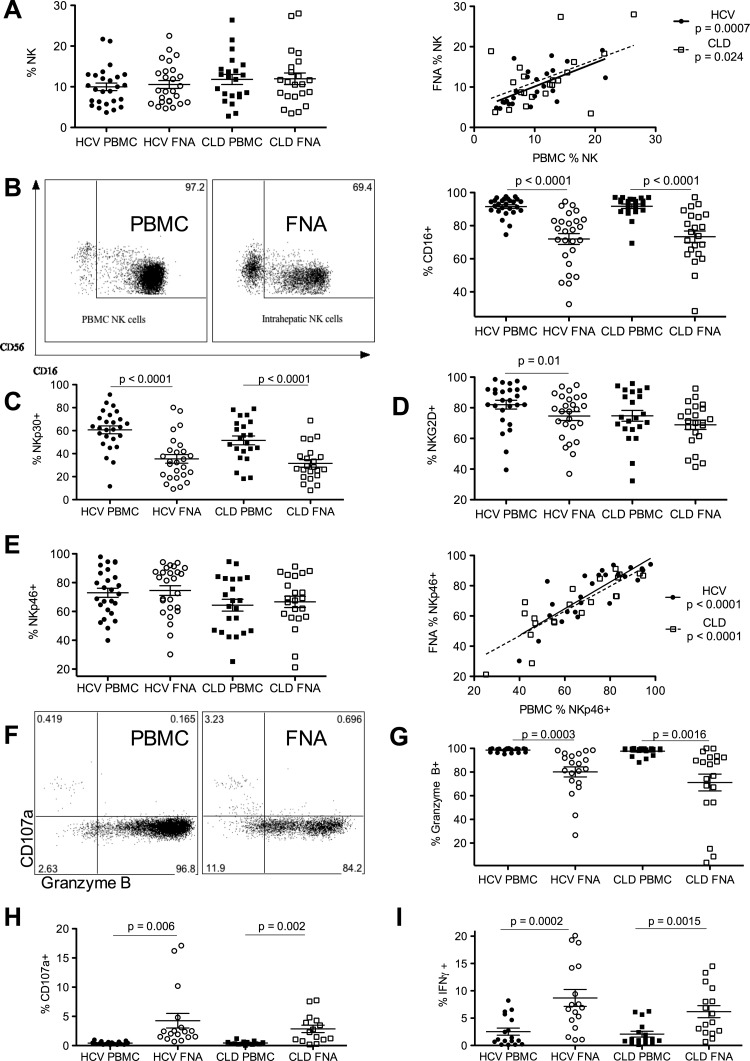
Figure 2.
Intrahepatic and peripheral blood natural killer (NK) cell phenotype and function. (A) NK cells as a percentage of lymphocytes in the peripheral blood and intrahepatic compartments of hepatitis C virus (HCV) and chronic liver disease (CLD) donors (left panel). The correlation of NK cells in the blood and intrahepatic compartments of HCV and CLD donors (p=0.0007, r2=0.4 and p=0.024, r2=0.23, respectively, right panel). (B) Representative fluorescence-activated cell sorter (FACS) plots of CD16 expression on NK cells in the peripheral blood mononuclear cell (PBMC) and the intrahepatic compartments (fine needle aspiration; FNA). NK cell CD16 expression is reduced in the intrahepatic compartment in the HCV and CLD cohorts (p>0.0001). (C) NKp30 expression is reduced in the intrahepatic compartment in the HCV and CLD cohorts (p<0.0001). (D) NKG2D expression is reduced in the intrahepatic compartment in the HCV cohort (p=0.01) but not in the CLD cohort. (E) NKp46 expression is not significantly different in the intrahepatic and peripheral blood compartments. Correlation of peripheral blood and intrahepatic NKp46 expression in the HCV and CLD cohorts (p<0.0001, r2=0.68). (F) Representative FACS plots of NK cell CD107a externalisation and intracellular granzyme B from peripheral blood and FNA. (G) Intracellular granzyme B is reduced in NK cells from the intrahepatic compartment in both the HCV (p=0.0003) and CLD cohorts (p=0.0016). (H) CD107a is increased in the intrahepatic compartment in the HCV (p=0.006) and CLD (p=0.002) cohorts. (I) Interferon (IFN)γ production is increased in NK cells in the intrahepatic compartments in the HCV (p=0.0002) and CLD (p=0.0015) cohorts. Mean and SEM shown.
Activating NK cells experimentally in vitro results in both degranulation (CD107a externalisation, figure 1C) and downregulation of cell surface NK activating receptors (eg, CD16, NKp30, NKp46 and NKG2D, see supplementary figure S3A–D, available online only). Detailed ex-vivo phenotypic analyses, without restimulation, confirm that intrahepatic NK cells have been activated in situ indicated by a highly significant downregulation in CD16 and NKp30 in HCV and CLD groups (p < 0.0001; figure 2B,C); downregulation in NKG2D expression (HCV cohort only p=0.01; figure 2D); and significantly increased expression of IFN-γ and CD107a with decreased intracellular granzyme B (p<0.006; figure 2F–I).
NKp46 was again distinguished from other activation markers as it did not show evidence of being downregulated within the liver, that is, the frequencies of NKp46+ NK cells in the blood and liver compartments were the same (figure 2E, left panel), with a highly significant correlation between the levels found in these compartments (p<0.0001, r2=0.68; figure 2E, right panel). HCV-infected subjects demonstrate higher levels of NKp46 in both blood and liver compared to CLD controls (figure 2E); and also slightly higher levels of NKp30 (figure 2C) and NKG2D (figure 2D). Furthermore, NKp46+ NK cell frequencies appeared to cluster intrahepatically into two groups (high frequencies >80%; low frequencies <70%, see supplementary figure S4, available online only)—the functional consequences of this are highlighted below.
In summary, despite in-situ inflammatory stimuli from chronic hepatitis and HCV infection activating intrahepatic NK cells (evidenced by downregulating certain NK cytotoxicity receptors, increased IFNγ production and degranulation; figure 2B–D,F–I), NKp46 does not appear to be downregulated.
NKp46-rich NK populations demonstrate increased activity with consequent pathology
The above data suggest HCV infection impinges on NKp46, and has a direct bearing on NK cell function. Twenty-four pretreatment liver biopsies were available from HCV-infected subjects. These were scored for the degree of necroinflammation (NI score); representative histology slides demonstrating lower and higher NI scores are shown (figure 3A). Portal tract inflammation is a striking feature of HCV infection; specialised stains for NKp46 and CD3 highlighted this portal inflammation, confirming the influx of NKp46+ NK cells are focused on the portal areas (figure 3B). This relationship between the frequency of intrahepatic NKp46+ NK cells (measured by flow cytometry) and hepatic inflammation (scored histologically) is demonstrated by the correlation with overall liver inflammation (using NI scores, p=0.007, Spearman's r=0.55; figure 3C, left panel) and even more significantly with portal inflammation score (p=0.004, Spearman's r=0.59; figure 3C, right panel). Importantly, in the CLD cohort (n=22) there was no association between NK cell phenotype, including NKp46 and functional markers and liver inflammation; suggesting an HCV-specific, rather than a general inflammatory process associating with NKp46 (data not shown).
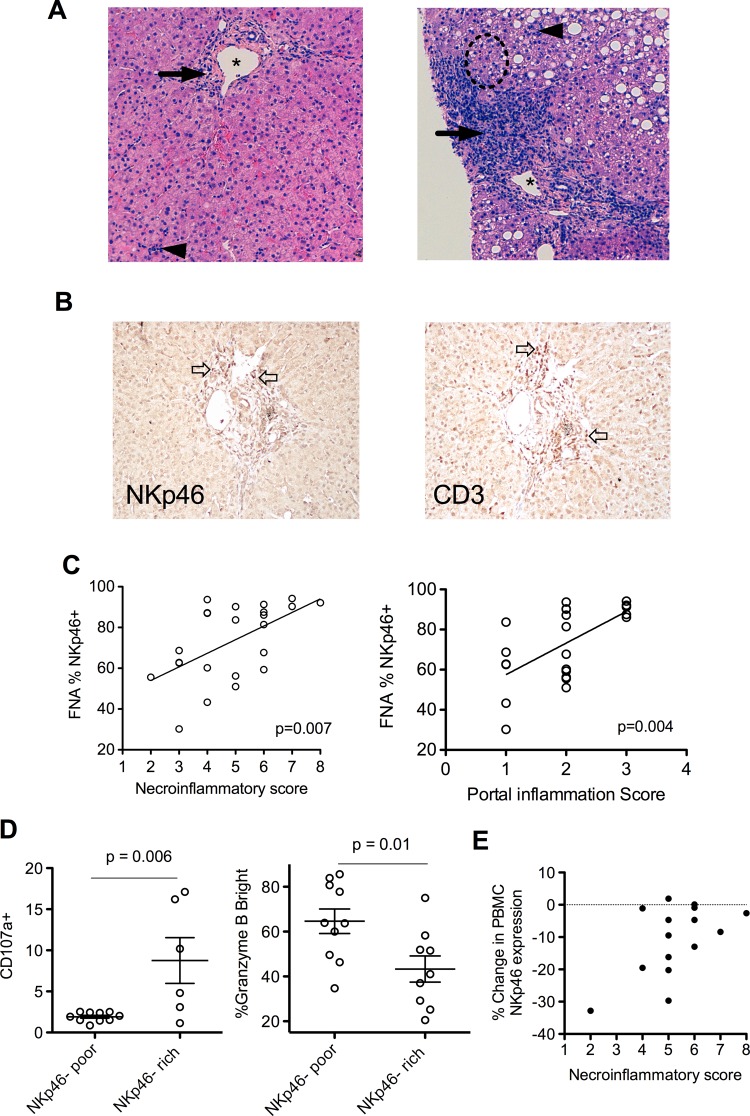
Figure 3.
NKp46-rich natural killer (NK) cell populations are more active and correlate with liver inflammation in chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV). (A) Representative H&E stain liver biopsies. Left panel—necroinflammatory score of 3 (*=portal tract, →=periportal inflammation, score=2, ◄=focal hepatitis, score=1) 30% NK cells NKp46+. Right panel—necroinflammatory score of 8, (periportal inflammation=3, interface hepatitis within broken circle=3, focal hepatitis=2) 92% NK cells NKp46+. (B) DAB immunohistochemistry of a portal tract from a HCV-infected individual demonstrating representative staining of NKp46+ cells (left panel two examples denoted by 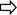 ) and CD3+ cells (right panel, 2 examples denoted by
) and CD3+ cells (right panel, 2 examples denoted by 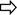 ). (C) %NKp46+ NK cells correlates with necroinflammatory score (p=0.007 Spearman's r=0.55), and in particular with portal inflammation (p=0.004, Spearman's r=0.59). (D) NKp46-rich intrahepatic NK populations have increased CD107a externalisation (left panel p=0.006) and reduced intracellular granzyme B in the HCV cohort (right panel p=0.01). (E) Reduction in peripheral blood NKp46+ NK cells after high-level stimulation and degranulation and necroinflammatory score. Mean and SEM shown. FNA, Fine needle aspiration; PBMV, peripheral blood mononuclear cells.
). (C) %NKp46+ NK cells correlates with necroinflammatory score (p=0.007 Spearman's r=0.55), and in particular with portal inflammation (p=0.004, Spearman's r=0.59). (D) NKp46-rich intrahepatic NK populations have increased CD107a externalisation (left panel p=0.006) and reduced intracellular granzyme B in the HCV cohort (right panel p=0.01). (E) Reduction in peripheral blood NKp46+ NK cells after high-level stimulation and degranulation and necroinflammatory score. Mean and SEM shown. FNA, Fine needle aspiration; PBMV, peripheral blood mononuclear cells.
An increased frequency of NKp46+ NK cells in blood is associated with increased activation (degranulation) on stimulation in vitro only in HCV-infected subjects (figure 1D). NKp46-rich intrahepatic NK cell populations are associated with more active liver inflammation (figure 3C). The possibility remained that an increase in these intrahepatic NK cells was a result of preferential trafficking of NKp46+ cells to the inflamed liver or upregulation of NKp46 within the inflamed liver. If this was the case we might expect to see a relative enrichment of NKp46+ cells compared to peripheral blood, but this was not seen. As stated above, there is a strong correlation between intrahepatic and peripheral blood NKp46 expression (figure 2E) with the levels within each subject, irrespective of the degree of liver inflammation, matching between compartments. To address this further, NK cell function was examined directly ex vivo. As outlined above, the proportion of intrahepatic NK cells expressing NKp46 separated the HCV cohort into two distinct clusters (NKp46-rich: ≥80% NKp46+ cells and NKp46-poor: ≤70% NKp46+ cells; figure 2E and supplementary figure S4, available online only). The NKp46-rich intrahepatic NK cell population demonstrated an increased activation compared to the NKp46-poor population as marked by degranulation (CD107a increased, p=0.006; figure 3D, left panel panel; intracellular granzyme B decreased, p=0.01; figure 3D, right panel). It has recently been demonstrated that the unknown ligand for NKp46 in HCV infection is expressed in vitro by a hepatoma cell line transfected with the JFH-1 HCV strain.18 This finding suggests that NKp46+ NK cells have the potential to be activated directly by HCV-infected hepatocytes. Overall, these data strongly support the notion that in-situ increased activation of NKp46-rich populations in the context of chronic HCV infection are a driving force in liver inflammation. We hypothesised that persistent overexpression of NKp46 within the NK population may allow these cells to engage continuously with putative activating ligands in vivo contributing to liver pathology. NKp46 is downregulated on NK cell activation in healthy individuals (see supplementary figure S3C, available online only). However, in HCV infection there appears to be a potential loss of this homeostatic mechanism in some individuals; individuals with the highest levels of liver inflammation (NI score) fail to downregulate NKp46 in ex-vivo degranulation assays at maximal stimulation (figure 3E). These data suggest that the mechanism of HCV-related immunopathology is a failure of intrinsic homeostatic NK cell attenuation within the chronically infected liver.
The relationship between IFNα treatment with blood and intrahepatic NKp46+ NK cells
Preliminary data suggested baseline NKp46 expression might influence the rate of viral clearance.17 We extended this study using serial blood samples in 17 subjects to calculate the rate of viral clearance (k in day−1) for each subject (examples shown in figure 4A). Indeed, the frequency of NKp46+ NK cells pretreatment did inversely correlate with the rate of viral clearance (p=0.01, r2=0.36; figure 4B), which is a strong predictor of HCV treatment success.19 So it appears that individuals with a high frequency of NKp46+ NK cells, which we have shown are more activated at baseline (figure 3C,D) are those least able to control the virus on IFNα treatment. This observation is borne out by measuring the capacity of the NK cells to increase their response from a weaker stimulus (Huh7.5 plus 50 IU/ml IFNα) to that of a stronger stimulus (K562 plus 1000 IU/ml IFNα); this increase is calculated as a functional ratio=% CD107a+ with strong stimulus÷% CD107a+ with a weak stimulus (as outlined in the Methods section). The functional ratio correlated inversely to the percentage of NKp46+ cells (p=0.005, r2=0.29; figure 4C) and there was a positive correlation with the rate of viral clearance (p=0.029, r2=0.3; figure 4D). In summary, NKp46 expression dictates the relative ability of NK cells to respond to increasing IFNα stimulation, which in turn reflects their ability to clear HCV rapidly during treatment. In keeping with this we found that individuals who achieved SVR following IFNα and ribavirin treatment had a lower mean frequency of NKp46+ NK cells than individuals who failed treatment (72% and 80.5%, respectively p=0.048, figure 4E).
Finally, having established the methodology for comparing side-by-side intrahepatic and blood-derived NK cell populations, we proceeded to obtain serial biopsies from nine patients with repeated FNA sampling at multiple time points during the first 12 weeks of treatment (figure 4F–I). After 12 weeks, seven patients had undetectable viral loads by PCR (and six of these eventually achieved an SVR) and two had no response to treatment. IFNα induced a significant increase in intrahepatic NK cells at days 1 and 3, but was not altered from baseline at later time points (p=0.008 repeated measures analysis of variance). The intrahepatic NK cells approximately doubled over 3 days (figure 4F) from the baseline mean of 10% (day 1 mean=16.0%, p=0.02; day 3 mean=17.8%, p=0.02; paired t test). Changes in percentage of CD16+, CD107a+ and NKp46+ (figure 4G–I) that occurred at days 1 and 3 returned to baseline by day 7. These changes occurred in the intrahepatic NK cells, and suggested activation with a small increase in CD107a and decrease in CD16. Again the behaviour of NKp46 was unexpected in as much as it actually increased at day 1. These changes overall were of a small magnitude, and there were no discernible differences in the changes measured prospectively in NK cell phenotype between the rapid responders and those who failed treatment in this cohort. However, an inability to distinguish between recent liver emigrants and the established intrahepatic NK cell population potentially masks significant alterations in the resident NK cell population.
Discussion
In HCV infection chronic liver inflammation results in fibrosis, cirrhosis and increases the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma. There is some evidence that NK cells are an important component of the innate immune response to HCV.5 9 11–13 The findings of this study corroborate the findings of Ahlenstiel et al,5 supporting an important role for NK cell cytotoxic function in contributing to the rapid early decline in viral load, a predictor of successful treatment. The data are also in keeping with our previous findings, which demonstrated that rapid viral clearance effectively abrogates the need and/or the ability to mount an adaptive immune response.17 This is in keeping with evidence from mouse models that highly active NK cells can clear viral antigen before adaptive immune priming.20 21 However, failure of both innate and CD4 T-cell responses to IFNα results in treatment failure.17
In this paper we further investigated NK cell activity in both blood and liver of HCV-infected individuals. We have utilised a FNA technique for sampling intrahepatic NK cells, which has allowed repeated sampling of the same individual at multiple time points during IFNα-based treatment of HCV for the first time. In order to reduce contamination from peripheral lymphocytes the needle is inserted 2–4 cm in an attempt to avoid puncture of the larger central branches of veins or arteries; any markedly bloody samples were discarded and the procedure repeated. FNA NK cells demonstrated a highly significant shift in phenotype and functional markers (figure 2). However, as the liver is an extremely vascular organ there remains the possibility that some of the lymphocytes may have been sampled from small blood vessels within the liver capsule rather than within the liver parenchyma itself. NK cells were initially reported to account for 30–50% of lymphocytes within the intrahepatic compartment.22 However, we found that this proportion was lower and strongly correlated with the proportion of NK cells in the peripheral blood (mean 10.5% and 9.6%, respectively, figure 2A). These proportions of CD3+ and NKp46+ lymphocytes were similar on immunohistological staining (figure 3B). The lower proportion of intrahepatic NK cells is in keeping with the findings of multiple studies, which report a mean intrahepatic NK cell proportion ranging from 2.7% to 18%.7 11 13 14 23 24 NK cells with a high frequency of NKp46 expression, termed NKp46 rich, from the intrahepatic compartment of HCV-infected subjects have a more activated phenotype. In line with this, we found significantly higher necroinflammatory scores were observed in NKp46-rich individuals. The ligands of activating receptors such as NKp30 and NKp46 are poorly characterised. Viral haemagglutinins from influenza, ectromelia and vaccinia viruses have been shown to engage with NKp30 and/or NKp46.25 26 In vaccinia infection, the viral haemagglutinin actually blocks NKp30 activation. In addition, NKp30 has also been shown to bind to a stress ligand B7-H6 expressed on tumour cells including the K562 cells.27 The presence of the ligand for NKp46 has been identified on HCV-infected hepatocytes indirectly using NKp46-Fc fusion proteins, but the nature of the actual ligand is unknown.18 Considering these results, it is striking that during IFNα treatment the ability to respond robustly to the increasing level of stimulation from IFNα is found in individuals with NKp46-poor NK populations, in whom there is an associated rapid decline in viral load and treatment success. This presents a paradox that patients most in need of treatment (high inflammation, greatest long-term risk) may be more difficult to treat.
Two recent studies have identified NKp46High NK cells as also being more activated in HCV infection.13 18 In these studies NK cell subpopulations were defined using the level of NKp46 expression on a per-cell basis using the mean fluorescence intensity (MFI). These studies suggest that on the basis of in-vitro assays, these NKp46High cells have greater antiviral activity. We found that NKp46 expression, based on MFI, formed a single population (rather than two discrete high and low subpopulations) in 40% of our cohort, which may relate to methodological differences between the studies (see supplementary figure S6A, available online only). However, we do find NKp46 MFI correlates strongly with the percentage of NKp46+ cells (p<0.0001, see supplementary figure S6B, available online only). We also find NKp46 is associated with NK cells with greater cytoxic potential in vitro (figure 1D) and increased activation measured ex vivo (figure 3D). However, cytotoxic/antiviral activity measured in vitro does not translate to in-vivo treatment-induced control of the virus. It is the ability to ncrease NK cell activity significantly i(ie, the functional ratio shown in figure 4C,D), as found in NKp46-poor populations, as a potentially abrupt escalation of the cytotoxic attack that is important. This concept of relative response to IFNα is in keeping with previous findings of interferon-stimulated genes (ISG) in chronic HCV infection suggesting a common theme to treatment resistance. Individuals with low ISG expression before treatment who have marked upregulation of ISG on initiation of IFNα are more likely to achieve SVR than those with high ISG expression pretreatment.28–30
Measurement of the frequency of NKp46+ NK cells might serve as a biomarker to help predict treatment outcome. NKp46 may serve two purposes in the development of HCV treatment strategies as a therapeutic target. First, blockade of NKp46 might reduce NK cell activity before IFNα treatment and improve the subsequent NK cell response. Second, NKp46 blockade may reduce inflammation as a long-term treatment goal in those unable to undergo IFNα treatment. We are currently conducting studies to explore these ideas.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the hepatology and infectious diseases specialist nurses at University Hospital of Wales for their help with this study. They also thank Kathryn Smart and Hayley Bridgeman for their expert laboratory assistance.
Footnotes
Contributors: TP: conducted sample collection, performed experiments and analysis and co-wrote paper. AC: clinical histology review and scoring. EJ: immunohistology. RKH: statistical analysis. ECYW: study review and analysis. AMG: study supervision, design and analysis and co-wrote paper. AG: study supervision, design and analysis and co-wrote paper.
Funding: Financial support for viral load measurement was supported by an educational grant from Roche Products Ltd. TP is supported by educational grants from the Welsh Assembly Government and the European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases. AMG holds a Wellcome Trust university award (reference no. 086983/Z/08/Z).
Competing interests: None.
Ethics approval: The study protocol conforms to the 1975 Declaration of Helsinki and the South East Wales Local Research Ethics Committee reviewed this project (04/WSE03/14 & 10/WSE02/45).
Provenance and peer review: Not commissioned; externally peer reviewed.
References
- 1.Day C, Lauer G, Robbins G, et al. Broad specificity of virus-specific CD4+ T-helper-cell responses in resolved hepatitis C virus infection. J Virol 2002;76:12584–95 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Godkin A, Jeanguet N, Thursz M, et al. Characterization of novel HLA-DR11-restricted HCV epitopes reveals both qualitative and quantitative differences in HCV-specific CD4+ T cell responses in chronically infected and non-viremic patients. Eur J Immunol 2001;31:1438–46 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Golden-Mason L, Cox AL, Randall JA, et al. Increased natural killer cell cytotoxicity and NKp30 expression protects against hepatitis C virus infection in high-risk individuals and inhibits replication in vitro. Hepatology 2010;52:1581–9 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Knapp S, Warshow U, Ho KM, et al. A polymorphism in IL28B distinguishes exposed, uninfected individuals from spontaneous resolvers of HCV infection. Gastroenterology 2011;141:320–5 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Ahlenstiel G, Titerence RH, Koh C, et al. Natural killer cells are polarized toward cytotoxicity in chronic hepatitis C in an interferon-alfa-dependent manner. Gastroenterology 2010;138:325–35 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Oliviero B, Varchetta S, Paudice E, et al. Natural killer cell functional dichotomy in chronic hepatitis B and chronic hepatitis C virus infections. Gastroenterology 2009;137:1151–60 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Sene D, Levasseur F, Abel M, et al. Hepatitis C virus (HCV) evades NKG2D-dependent NK cell responses through NS5A-mediated imbalance of inflammatory cytokines. PLoS Pathog 2010;6:e1001184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Nattermann J, Feldmann G, Ahlenstiel G, et al. Surface expression and cytolytic function of natural killer cell receptors is altered in chronic hepatitis C. Gut 2006;55:869–77 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Bozzano F, Picciotto A, Costa P, et al. Activating NK cell receptor expression/function (NKp30, NKp46, DNAM-1) during chronic viraemic HCV infection is associated with the outcome of combined treatment. Eur J Immunol 2011;41:2905–14 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Dessouki O, Kamiya Y, Nagahama H, et al. Chronic hepatitis C viral infection reduces NK cell frequency and suppresses cytokine secretion: reversion by anti-viral treatment. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2010;393:331–7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Bonorino P, Ramzan M, Camous X, et al. Fine characterization of intrahepatic NK cells expressing natural killer receptors in chronic hepatitis B and C. J Hepatol 2009;51:458–67 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Edlich B, Ahlenstiel G, Azpiroz AZ, et al. Early changes in interferon signaling define natural killer cell response and refractoriness to interferon-based therapy of hepatitis C patients. Hepatology 2012;55:39–48 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Kramer B, Korner C, Kebschull M, et al. Natural killer p46(High) expression defines a natural killer cell subset that is potentially involved in control of hepatitis C virus replication and modulation of liver fibrosis. Hepatology 2012;56:1201–13 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Varchetta S, Mele D, Mantovani S, et al. Impaired intrahepatic natural killer cell cytotoxic function in chronic hepatitis C virus infection. Hepatology 2012;56:841–9 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Ishak K, Baptista A, Bianchi L, et al. Histological grading and staging of chronic hepatitis. J Hepatol 1995;22:696–9 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Alter G, Malenfant JM, Altfeld M. CD107a as a functional marker for the identification of natural killer cell activity. J Immunol Methods 2004;294:15–22 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Pembroke T, Rees I, Gallagher K, et al. Rapid early innate control of hepatitis C virus during IFN-alpha treatment compromises adaptive CD4(+) T-cell immunity. Eur J Immunol 2012;42:2383–94 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Golden-Mason L, Stone AE, Bambha KM, et al. Race- and gender-related variation in natural killer p46 expression associated with differential anti-hepatitis c virus immunity. Hepatology 2012;56:1214–22 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Davis GL, Wong JB, McHutchison JG, et al. Early virologic response to treatment with peginterferon alfa-2b plus ribavirin in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology 2003;38:645–52 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Andrews DM, Estcourt MJ, Andoniou CE, et al. Innate immunity defines the capacity of antiviral T cells to limit persistent infection. J Exp Med 2010;207:1333–43 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Narni-Mancinelli E, Jaeger BN, Bernat C, et al. Tuning of natural killer cell reactivity by NKp46 and Helios calibrates T cell responses. Science 2012;335:344–8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Norris S, Collins C, Doherty DG, et al. Resident human hepatic lymphocytes are phenotypically different from circulating lymphocytes. J Hepatol 1998;28:84–90 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Kawarabayashi N, Seki S, Hatsuse K, et al. Decrease of CD56(+)T cells and natural killer cells in cirrhotic livers with hepatitis C may be involved in their susceptibility to hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2000;32:962–9 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Yamagiwa S, Matsuda Y, Ichida T, et al. Sustained response to interferon-alpha plus ribavirin therapy for chronic hepatitis C is closely associated with increased dynamism of intrahepatic natural killer and natural killer T cells. Hepatol Res 2008;38:664–72 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Mandelboim O, Lieberman N, Lev M, et al. Recognition of haemagglutinins on virus-infected cells by NKp46 activates lysis by human NK cells. Nature 2001;409:1055–60 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Jarahian M, Fiedler M, Cohnen A, et al. Modulation of NKp30- and NKp46-mediated natural killer cell responses by poxviral hemagglutinin. PLoS Pathog 2011;7:e1002195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Brandt CS, Baratin M, Yi EC, et al. The B7 family member B7-H6 is a tumor cell ligand for the activating natural killer cell receptor NKp30 in humans. J Exp Med 2009;206:1495–503 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Sarasin-Filipowicz M, Oakeley EJ, Duong FH, et al. Interferon signaling and treatment outcome in chronic hepatitis C. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2008;105:7034–9 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Chen L, Borozan I, Feld J, et al. Hepatic gene expression discriminates responders and nonresponders in treatment of chronic hepatitis C viral infection. Gastroenterology 2005;128:1437–44 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Su AI, Pezacki JP, Wodicka L, et al. Genomic analysis of the host response to hepatitis C virus infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2002;99: 15669–74 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.