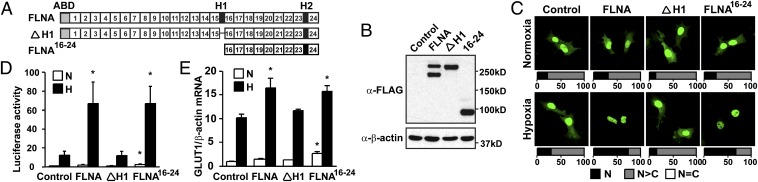
Fig. 6.
The C-terminal fragment of FLNA enhances nuclear accumulation and the transactivation function of HIF-1α. (A) Schematic representation of wild-type FLNA (FLNA), the cleavage-resistant FLNA mutant where H1 domain is deleted (ΔH1), and the truncated C-terminal FLNA containing repeats 16–24 (FLNA16-24). (B) Expression of wild-type FLNA and mutants in cell lines stably expressing FLNA, ΔH1, and FLNA16-24. Control cells were transfected with empty vector. (C) Nuclear localization of GFP-HIF-1α in hypoxia is increased in FLNA- and FLNA16-24-expressing cells. Quantifications are presented as described in SI Materials and Methods. (D and E) Transactivation activity of HIF-1α is up-regulated in FLNA- and FLNA16-24-expressing cells. HRE-driven luciferase reporter assay (D) and GLUT1 expression analyzed by quantitative RT-PCR analysis (E) were performed in the stable cell lines cultured in either normoxia (N) or hypoxia (H). Data are shown as mean ± SD of at least three independent experiments. *P < 0.05 compared with corresponding samples of control cells.