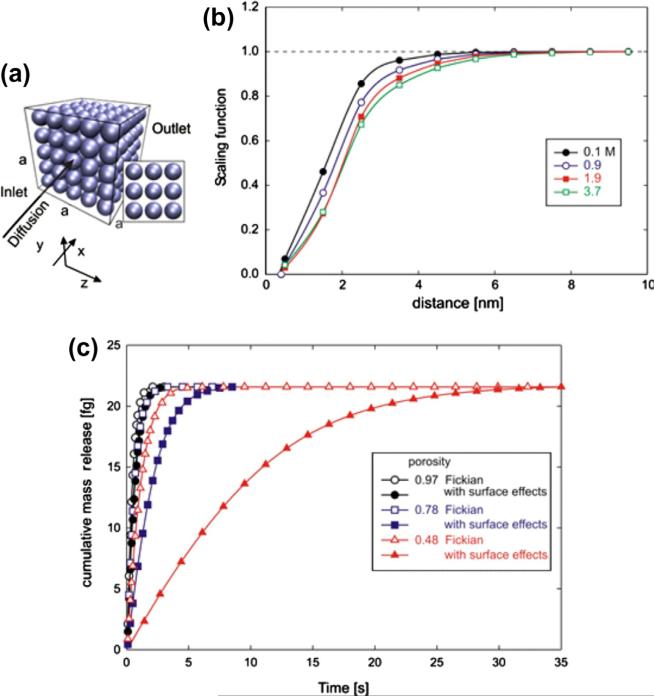
Fig. 7.
Diffusion through a porous medium consisting of packed silica nanospheres, microstructural model. (a) Internal structure of the medium; diffusion occurs from the inlet surface (attached to a reservoir with a prescribed volume and initial concentration c0) to the outlet with concentration c = 0. Porosity is 0.78; (b) Scaling functions used in the analysis, according to [7], for diffusion through water of glucose molecules and silica surfaces; (c) Mass release curves for Fickian diffusion (no surface effects) and diffusion with surface effects, for three different porosities; minimum porosity 0.48 corresponds to the case when the spheres are just touching. Surface effects are more pronounced for smaller porosities due to a relatively larger internal surface.