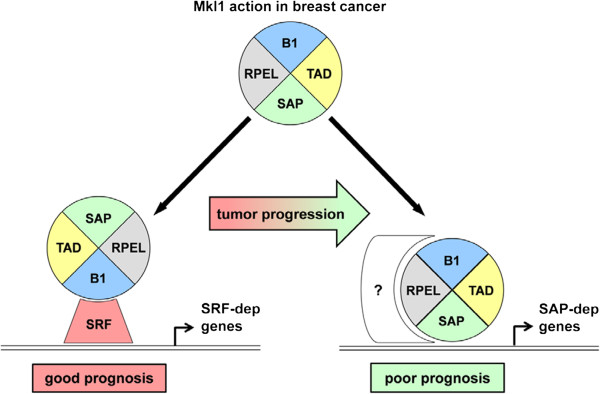
Figure 8.
Schematic representation of the Mkl1 action in breast cancer. A circular Mkl1 model is depicted with four of its domains: RPEL, actin binding motifs with RPxxxEL core consensus; B1, basic domain involved in SRF-binding; SAP, homology domain found in the nuclear proteins SAF-A/B, Acinus, PIAS; TAD, transactivation domain. Serum response factor is drawn as a red shape and putative unidentified DNA-binding proteins as white shape with a question mark. Mkl1 exerts two distinct modes of action: one of them is through the B1 domain required for serum response factor (SRF)-binding activity and induction of SRF/Mkl1 target gene expression; the other one is strongly dependent on the SAP domain and triggers the expression of a specific set of pro-proliferative and pro-migratory genes that we called SAP-dependent Mkl1 target genes. High expression of SRF-dependent genes is associated with good clinical outcome for breast cancer patients, whereas elevated expression of SAP-dependent targets correlates with poor prognosis and indicates a significant role for these genes in breast cancer progression.