Fig 2.
The effects of stauprimide (Spd) and activin A (A) concentrations and human embryonic stem cell (hESC) line on the efficiency of the Spd-A50 protocol.
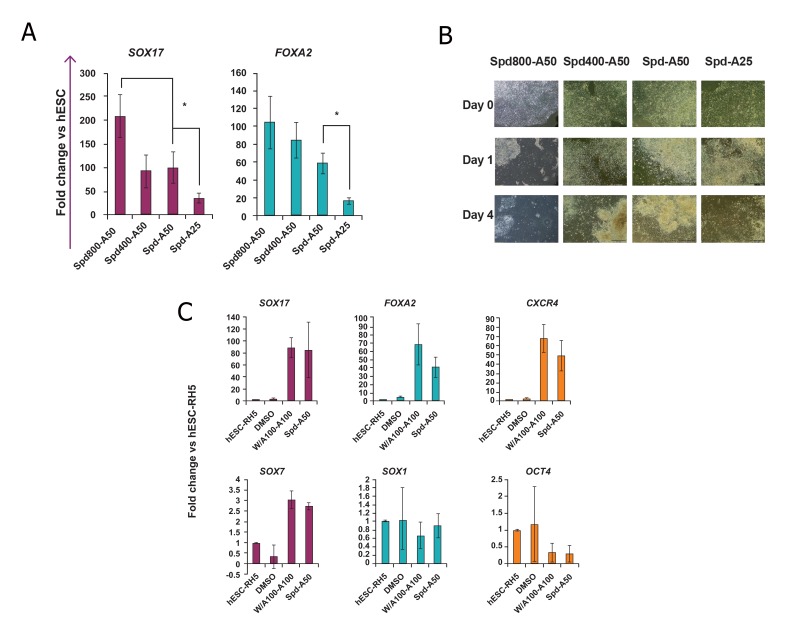
A. hESC-Rh6 were treated with Spd200/400/800-A50 and the Spd-A50 regimen. Samples were analyzed for expressions of SOX17 and FOXA2 by Q-PCR at the end of the fourth day. *; Significant difference from all other groups, at least p<0.05 as determined by ANOVA with Tukey’s LSD test. n=3-4.
B. Phase contrast images were taken at day 0 (hESC colonies at the beginning of the experiment), day 1 (the same colony, one day after treatment with Spd) and at day 4 (3 days after treatment with activin A). High mortality of the cells was observed after treatment with 800 nM Spd (Spd800-A50 group).
C. Lineage-specific gene expression analysis of Spd-A50-treated Royan H5 human embryonic stem cells (hESC-RH5). In control groups, hESCs were treated with 0.1% dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) for 4 days and considered as the negative control. Cells were treated with Wnt3a and activin A for the first day followed by activin A for the next three days (W/A100-A100) as the positive control. As determined by Q-PCR, the DE markers SOX17, FOXA2 and CXCR4 highly expressed in Spd-A50-treated Royan H5 hESCs while SOX7 [visceral endoderm (VE) marker], SOX1 (neuroectoderm marker) and OCT4 (pluripotency marker) exhibited low levels of expression. This expression pattern was similar to that obtained from the hESC-RH6 line. The target gene expression level was normalized to GAPDH and presented relative to hESC. Data are presented as mean ± SD.