Figure 3.
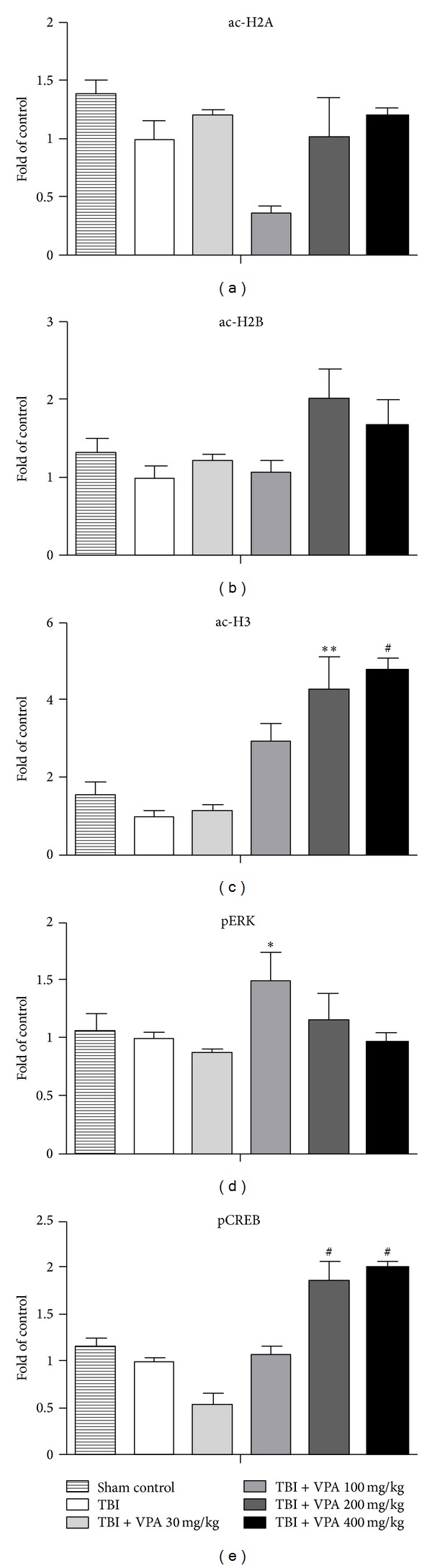
Systemic VPA administration increases H3 histone acetylation, p-ERK, and p-CREB in brain. The statistical analysis of the quantification of western blots (c) showed that systemic VPA administration (n = 3 per group) significantly increases histone H3 acetylation with the dosage of 200 mg/Kg (P = .0087) and 400 mg/Kg (P = .006) 1 day after treatment compared to the vehicle-treated controls. No significant changes were detected when the levels of acetyl-H2A and acetyl-H2B histone antibodies were evaluated (a and b). Significant increase of p-ERK expression was noted 1 day after 100 mg/kg VPA treatment compared to vehicle-treated controls (d), (P = .0488). Also increased expression of p-CREB was noted with the dosage of 200 mg/Kg (P < .0001) and 400 mg/Kg (P < .0001) 1 day after VPA treatment compared to the vehicle-treated controls (e). These results demonstrate that systemic VPA administration increases H3 histone acetylation, p-ERK, and p-CREB expressions in the brain.
