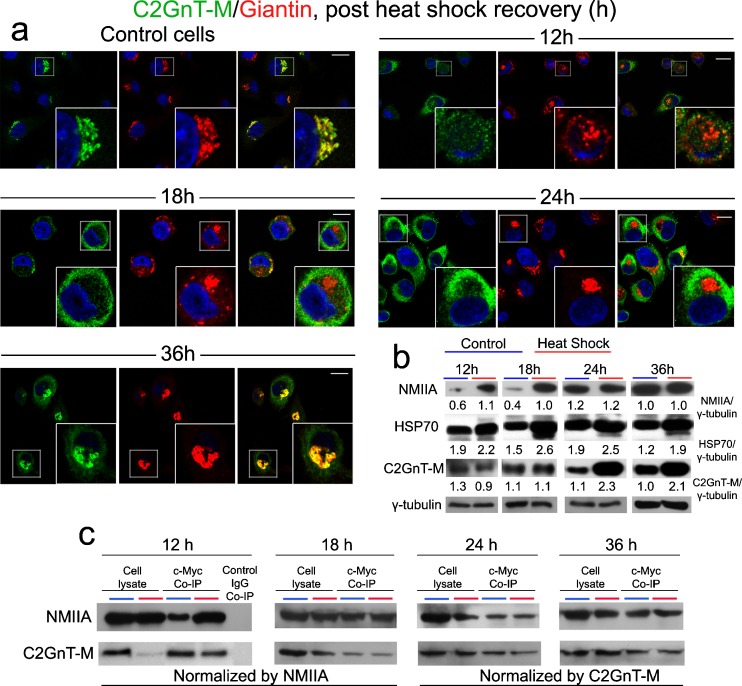
Fig. 3.
NMIIA is involved in cytoplasmic mobilization of bC2GnT-M in Panc1-bC2GnT-M (c-Myc) cells during post-heat shock recovery. a Cells were heat-shocked at 45 °C for 20 min and allowed to recover under normal growing conditions for up to 36 h. At 12 h post HS, C2GnT-M together with giantin moved out of the fragmented Golgi. At 18 h, the Golgi (giantin) was partially recovered; however, C2GnT-M was retained in the cytoplasm. At 24 h, Golgi morphology was restored and C2GnT-M was still in the cytoplasm. After 36 h of recovery, C2GnT-M returned to the Golgi. b NMIIA, HSP70, and bC2GnT-M (c-Myc) western blots of the lysates obtained from cells treated by HS and allowed to recover under normal growing condition for 12, 18, 24, and 36 h. Increased NMIIA was detected at 12 and 18 h; level of HSP70 was elevated throughout the entire recovery phase; decrease of C2GnT-M was found at 12 h; no change was found at 18 h; and increased C2GnT-M was detected at 24 and 36 h. Gamma-tubulin was used as a loading control. NMIIA, HSP70, C2GnT-M, and γ-tubulin bands were analyzed by densitometry and the data were presented after normalization with γ-tubulin value. c NMIIA and c-Myc western blot of complexes pulled down with anti-c-Myc Ab from the lysates of cells recovered after HS for 12, 18, 24, and 36 h. At 12 h, Golgi fragmentation occurred and NMIIA–C2GnT-M complexes were elevated. Cell lysate treated with nonspecific IgG served as the negative control. Lysates containing equal amounts of NMIIA (12 and 18 h) or C2GnT-M (24 and 36 h) were used for Co-IP. Representative pictures of at least three independent experiments are shown. All confocal images were acquired with same imaging parameters; bars, 10 μm