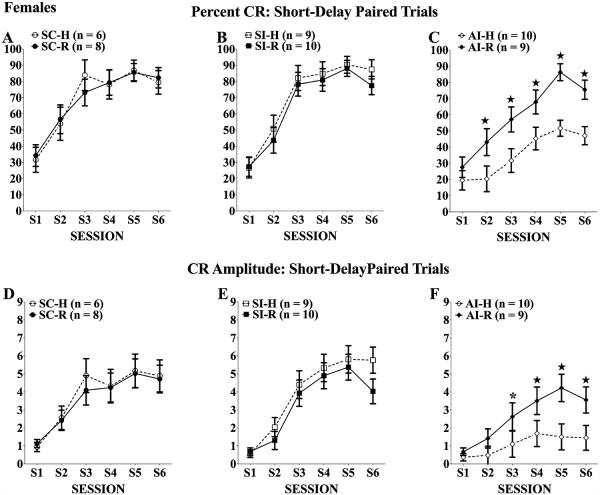
Fig. 3.
Percent (A–C)and amplitude (D–F) of conditioned responses (CRs) of females across 6 eyeblink training sessions. All rats increased the frequency of CRs elicited over training; however, neonatal alcohol treatment significantly impaired CR acquisition. Twenty days of complex motor learning significantly increased the percent CRs and the CR amplitudes of alcohol intubated (AI) group compared with the AI handled group (C and F). *Tukey’s post hoc p < 0.05; ★Tukey’s post hoc p < 0.01.