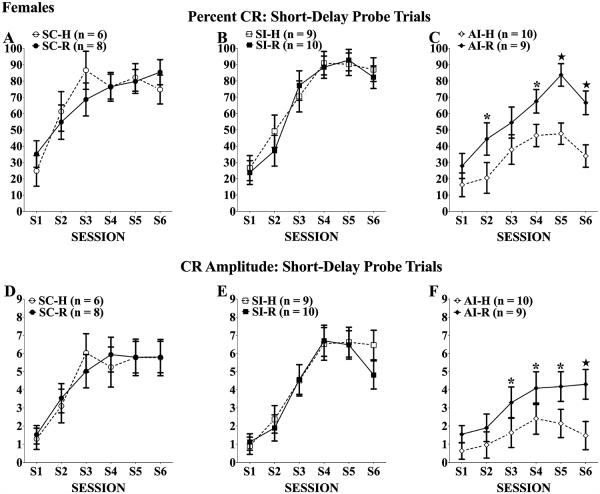
Fig. 4.
Percent (A–C)and amplitude (D–F) of conditioned responses (CRs) of females across 6 eyeblink training sessions. All rats increased the frequency of and amplitude CRs elicited during probe trials over training; however, neonatal alcohol treatment significantly impaired CR acquisition. Twenty days of complex motor learning failed to significantly improve CR frequency and amplitude among alcohol intubated (AI) rats (C and F). *Tukey’s post hoc p < 0.05; ★Tukey’s post hoc p < 0.01.