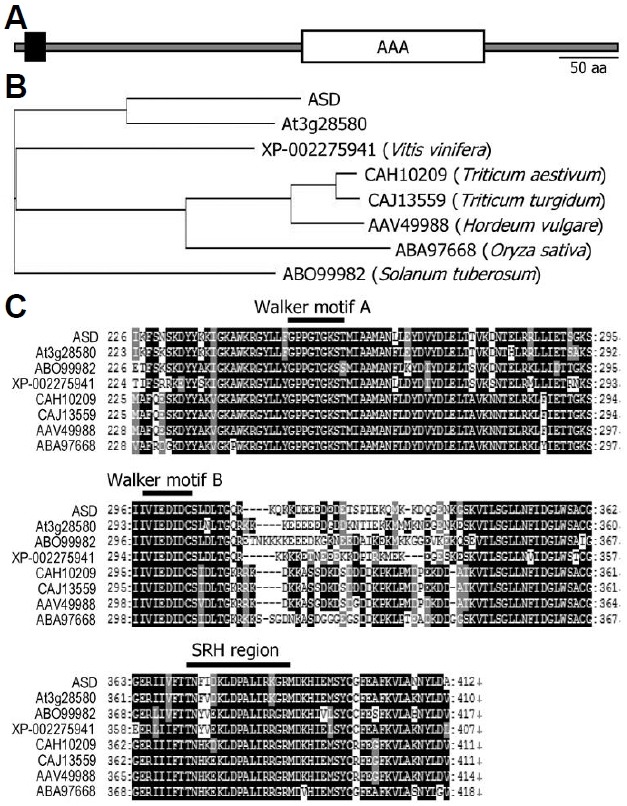
Fig. 1. Protein structure of ASD and phylogenetic analysis of ASD homologues in plants. (A) Protein structure of ASD. The ASD pro-tein contains a TM motif in the N-terminal region (black box) and an AAA domain in the C-terminal region (white box). The protein struc-ture was analyzed using the software available in the ExPASY da-tabase (http://us.expasy.org/tools/). (B) Phylogenetic analysis of ASD and its homologues from several plant species. The accession numbers of the protein sequences analyzed are XP-002275941 (grape vine, Vitis vinifera), CAH10209 (wheat, Triticum aestivum), CAJ13559 (wheat, Triticum turgidum), AAV49988 (barley, Hordeum vulgare), ABA97668 (rice, Oryza sativa), and ABO99982 (potato, Solanum tuberosum). (C) Sequence alignment of the AAA domain from ASD and its homologues. Black boxes indicate identical resi-dues, and gray boxes indicate biochemically conserved residues. The Walker A and B and SRH motifs are indicated above the se-quences. The amino acid sequence alignment was carried out using the ClustalW server (http://www.ebi.ac.uk/clustalw/).