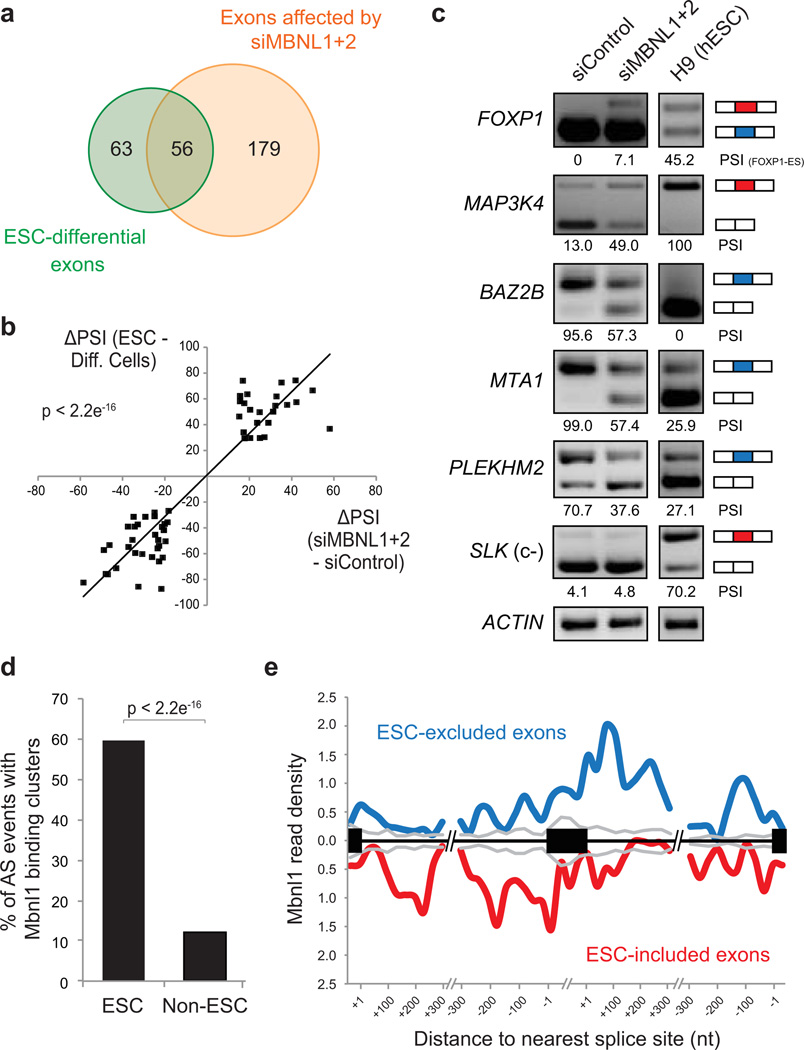
Figure 3. MBNL proteins regulate approximately half of ESC-differential alternative splicing events.
a) Venn diagram showing the proportion of ESC-differential AS events (green) that display ≥15 PSI change between HeLa cells transfected with siRNA pools targeting MBNL1+2 (siMBNL1+2) versus siControl pool (orange). b) High association (p<2.2e−16, one-sided binomial test between quadrants) between differences in PSIs of ESCs versus differentiated cells/tissues, and differences in PSIs of siMBNL1+2 knockdown versus siControl treatments. c) Representative RT-PCR validations for ESC-differential AS events that have PSI changes in HeLa cells following siMBNL1+2 transfection and for ESC-differential AS events that do not change upon siMBNL1+2 knockdown (c-); splicing patterns in human H9 ESCs are shown for comparison. d) Percentage of AS events with overlapping Mbnl1 CLIP-Seq binding clusters20 in C2C12 cells for ESC-differential or non-ESC-regulated alternative exons. e) Merged map of Mbnl binding clusters in transcripts with ESC-differential AS events. Maps of Mbnl1 binding sites with respect to exons that have higher or lower inclusion in ESCs/iPSCs, relative to non-ESCs/tissues.