Figure 1.
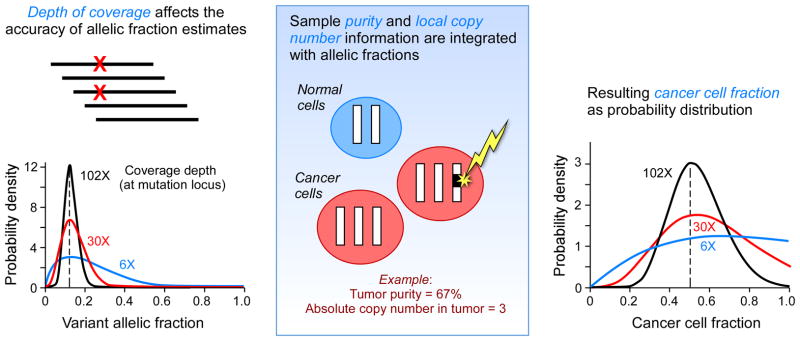
inferring the size of a subpopulation affected by somatic mutations from genomic data. Massively parallel sequencing provides an estimate of variant allelic fraction (VAF), which is calculated by counting the number of reads with the variant alleles and dividing it by the total number of reading from the specific location. The certainty of the estimate is a function of the depth of coverage, using binomial distribution (panel A). Subsequently, the VAF estimates are integrated with the purity and local copy number information (panel B) to yield cancer cell fractions (CCF, panel C). In the example provided a somatic mutation with a VAF of 0.125, a local copy number of 3 and a purity of 67% yields CCF estimates of 0.5.
