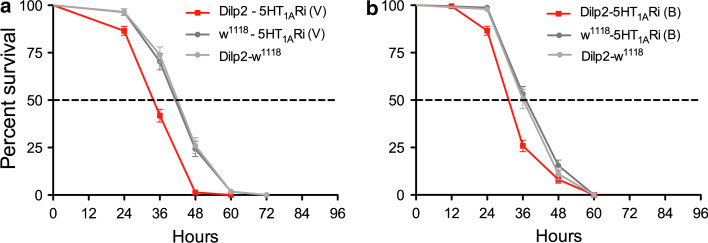
Fig. 5.
Knockdown of 5-HT1A receptor in IPCs increases sensitivity to starvation. We performed GABAB 5-HT1A receptor knockdown in IPCs with two different RNAi constructs, one from VDRC [5-HT1ARi(V)] (a) and another from Bloomington Stock Center [5-HT1ARi (B)] (b). These flies were crossed to a Dilp2-Gal4 driver [40] used in all experiments, unless other specified. Male flies were kept on aqueous agarose (to induce starvation) and their survival monitored over time. All experiments were run in three replicates. a Using a Dilp2-Gal4 driver to knockdown the 5-HT1A receptor in IPCs [Dilp2-5-HT1ARi (V)], we obtained flies that display significantly reduced survival at starvation (p < 0.0001 to both parental controls, Log rank test, Mantel-Cox; n = 111–215 for each genotype). b Flies obtained from crossing Dilp2-Gal4 with the other strain 5-HT1ARi (B) also displayed significantly reduced survival at starvation (p < 0.0001 and p = 0.0002 to the two controls; n = 159–209 for each genotype). In all subsequent graphs with 5-HT1ARNAi, we used the (V) strain. We also used a different Dilp2-Gal4 driver (on the 3rd chromosome) [18] to drive the UAS-5-HT1ARi(V) and obtained the same significantly reduced life span at starvation (see S. Fig. 3)