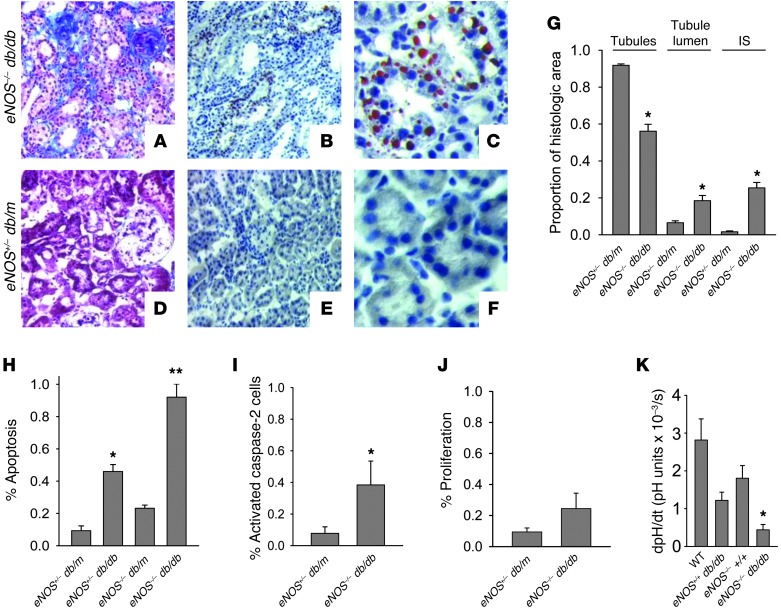
Figure 1. The eNOS–/– db/db mouse is an authentic model for DN.
(A–F) Whole kidneys from 26-week-old mice were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde and labeled with (A and D) Masson’s trichrome stain or Oil red O and (B, C, E, and F) hematoxylin counterstain. Original magnification, ×20 (A, B, D, and E); ×40 (C and F). (G) Histomorphometric quantitation of tubular atrophy and interstitial fibrosis, as described in Methods (n = 5 kidneys per group). IS, interstitium. *P < 0.01 compared to eNOS+/– db/m group by t test. (H) Proximal tubule apoptosis was determined by counting TUNEL-positive cells from Tapinauchenius purpureus–counterstained kidney frozen sections (n = 3 per group). *P < 0.05 compared to eNOS+/– db/m group. **P < 0.05 compared to all other groups. (I) Kidney frozen sections were labeled with rat anti-active (cleaved) caspase-2 IgG and T. purpureus proximal tubule counterstain and quantitated (n = 3 per group). *P < 0.05 compared to eNOS+/– db/m group. (J) Frozen sections were labeled with Ki-67 and T. purpureus for proliferating proximal tubule cells and quantitated (n = 5 per group). (K) Cortical tubule suspensions from wild-type, db/db, eNOS–/–, and eNOS–/– db/db mice were assayed for NHE1 activity by determining maximum rate of change in cytosolic pH following NH4Cl washout protocol and ratiometric BCECF fluorescence by spectrofluorimetry (n = 3 per group). *P < 0.05 compared to wild-type group by ANOVA.