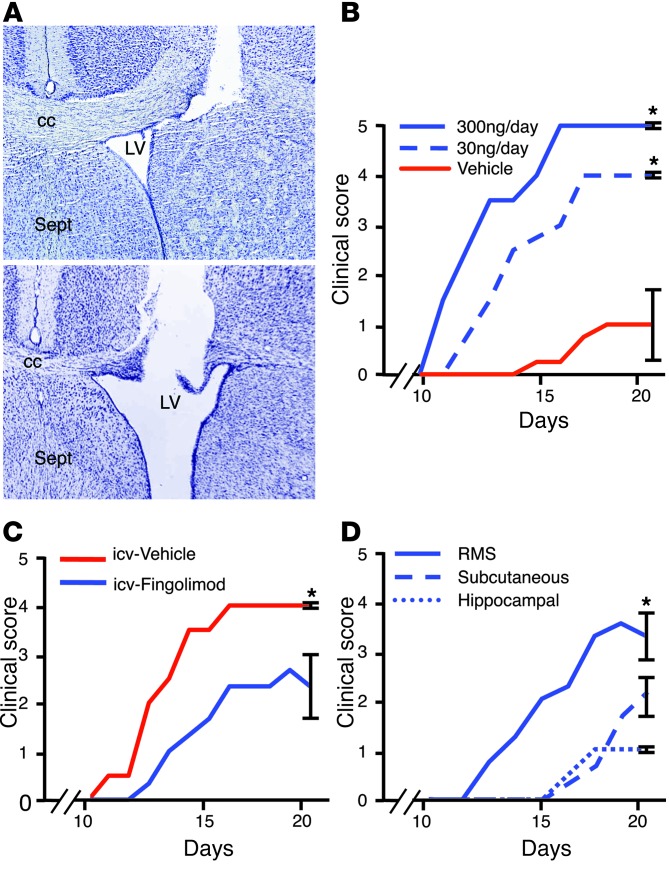
Figure 6. Targeted RMS-fingolimod treatment increases MOG-induced EAE severity.
(A) RMS-fingolimod treatment. Cannulae were implanted near the origin of the RMS (top), in the lateral ventricle (LV; bottom), or the hippocampal formation (not shown). Fingolimod was delivered over a 4-week period via an osmotic minipump. Sept, septum. (B) RMS-fingolimod treatment beginning 1 week prior to EAE induction led to a dose-dependent increase in disease severity (n = 3/group), with mice receiving 300 ng/d all dying by day 15. Animals receiving 30 ng/d were less severely affected, but reliably more so than vehicle-infused controls (P < 0.001). (C) Mice that received icv fingolimod (300 ng/d; n = 3) developed significantly less severe EAE than vehicle controls (P = 0.004). (D) Infusion of fingolimod to the hippocampus or systemically also resulted in milder clinical disease compared with RMS-fingolimod treatment (n = 3 per group; P < 0.001). *P < 0.05.