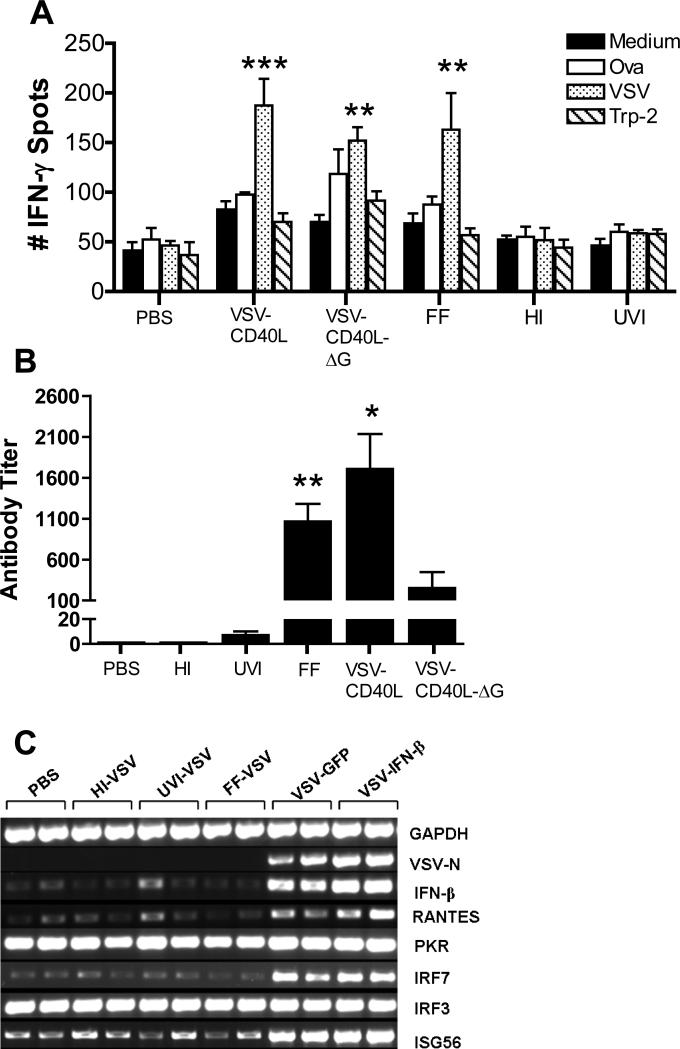
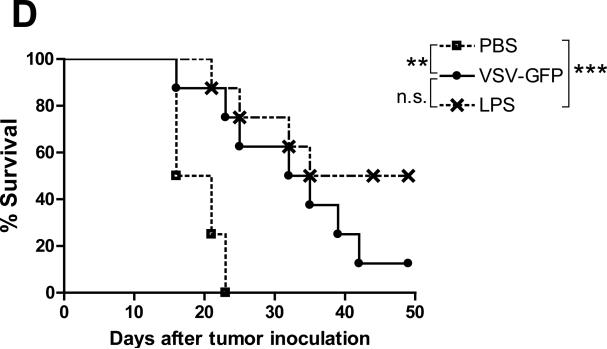
Figure 6. Immune responses after intratumoral injection of live and inactivated forms of VSV and therapeutic efficacy of intratumoral TLR agonist in B16ova tumors.
A. Subcutaneous B16ova tumors were infected with 3 daily injections of either live or inactivated VSV (5×107 pfu/injection). Eight days after the last virus, spleens were harvested, dissociated and incubated with one of the four antigens indicated. Total IFN-γ spots (1×105 splenocytes/48h) were measured using ELISPOT (n=3 mice/group). B. At the time of sacrifice (day 17 after tumor challenge), blood was also extracted and serum neutralizing antibody titer was determined. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001. C. RT-PCR for type I interferon-responsive genes was performed on total RNA from subcutaneous B16ova tumors—harvested 8 hours postinfection—given a single injection of 5×108 pfu either live or inactivated VSV. D. Kaplan-Meier survival plot of B16ova tumor-bearing C57Bl/6 mice (n=8 per group) treated with three (3) intratumoral injections of either VSV-GFP (5×108 pfu/dose) or 200 μg of lipopolysaccharide (LPS). *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001.