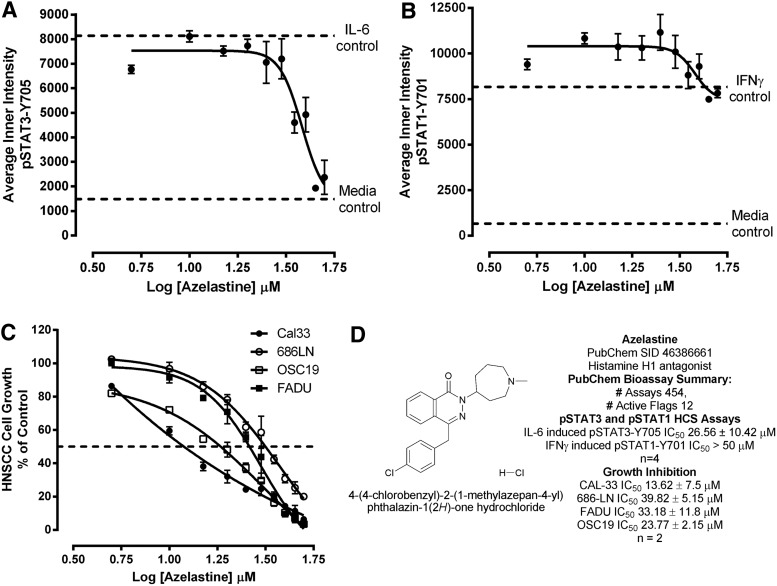
Fig. 8.
Concentration-dependent effects of azelastine on (A) IL-6 induced pSTAT3 activation, (B) IFNγ-induced pSTAT1 activation, (C) HNSCC cell growth inhibition, and (D) azelastine chemical structure and biological activity summary. (A) Inhibition of IL-6-induced pSTAT3 activation, and (B) inhibition of IFNγ-induced pSTAT1 activation. First, 2,000 Cal33 HNSSC cells that had been serum starved for 24 h as described earlier were exposed to the indicated concentrations of azelastine for 3 h. Next, those cells were treated with either 50 ng/mL of IL-6 or 30 ng/mL of IFNγ for 15 min at 37°C in 5% CO2 and 95% humidity, and were then fixed and stained with Hoechst and either a mouse monoclonal anti-p-STAT3-Y705 antibody or a mouse monoclonal anti-p-STAT1-Y701 antibody as described in Materials and Methods (Table 1). The mean±SD (n=3) average inner (nuclear) intensities of the p-STAT3-Y705 (A) or p-STAT1-Y701 (B) signals from triplicate wells for each compound concentration are presented. Representative experimental data from one of three independent experiments are shown.(C) HNSCC growth inhibition. First, 1,000 Cal33, 686LN, FaDu, or OSC19 HNSCC cells were seeded into 384-well assay plates and incubated at 37°C in 5% CO2 and 95% humidity for 24 h. After 24 h, the indicated concentrations of azelastine were transferred into the test wells of the 384-well assay plates that were then incubated at 37°C in 5% CO2 and 95% humidity for an additional 72 h. Control wells received DMSO alone. After 72 h of exposure to azelastine, Cell Titer Glo detection reagent was dispensed into the wells of the assay plates, and the luminescent signal was captured on the Envision microtiter plate reader. The mean±SD (n=3) growth inhibition data from triplicate wells for each concentration of azelastine are presented as the % of the DMSO plate controls; Cal33 (•), 686LN (○), FaDu (▪), and OSC19 (□). Representative experimental data from one of three independent experiments are shown. (D) Azelastine chemical structure and biological activity summary of the chemical structure of azelastine, (RS)-4-[(4-chlorophenyl)methyl]-2-(1-methylazepan-4-yl)-phthalazin-1-one, is presented along with a summary of the IC50 values for azelastine in the IL-6-induced pSTAT3 activation assay, the IFNγ-induced pSTAT1 activation assay, and the HNSCC growth inhibition assays, and the results of a cross-target query of the biological activity of SID 46386661 in the PubChem database. IC50, 50% inhibition concentration.