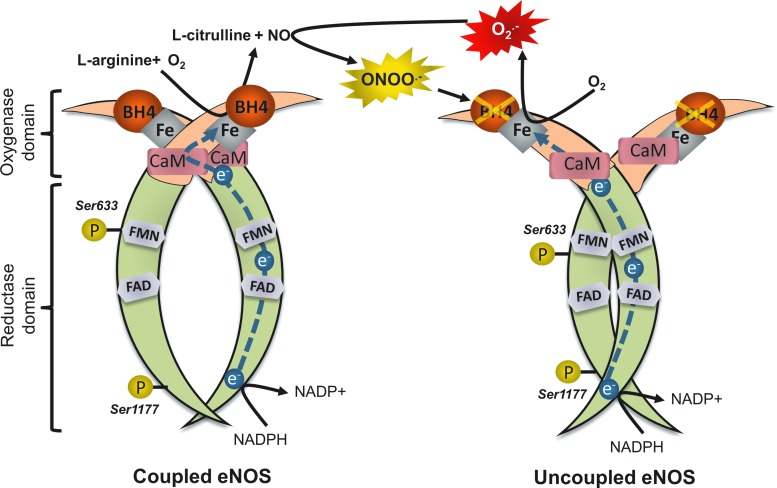
FIG. 1.
Uncoupling of eNOS. In the presence of BH4, eNOS shuttles electrons from the flavins of the reductase domain of one monodimer to the oxygenase domain of the other monodimer, in a two-step reaction that produces l-citrulline and NO from l-arginine and O2. BH4 is sensitive to degradation by ROS, especially ONOO−. In the absence of BH4, eNOS is uncoupled; electrons are transferred to O2, producing O2−. O2− reacts rapidly with NO to form ONOO−, which can further oxidize BH4, creating a vicious circle that leads to endothelial dysfunction. Ser-1177 and Ser-633 are activation phosphorylation sites, which are hypothetical targets of statins. eNOS, endothelial nitric oxide synthase; BH4, tetrahydrobiopterin; O2−, superoxide; ONOO−, peroxynitrite; ROS, reactive oxygen species; NO, nitric oxide. To see this illustration in color, the reader is referred to the web version of this article at www.liebertpub.com/ars