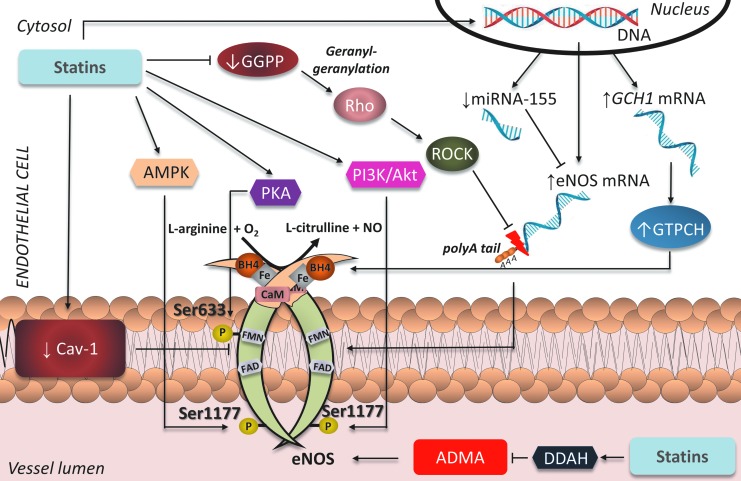
FIG. 4.
Effects of statins on eNOS in ECs. By inhibiting mevalonate synthesis, statins reduce GGPP, preventing activation of Rho/ROCK and stabilizing eNOS mRNA, thus increasing eNOS expression. By reducing caveolin-1 content and circulating ADMA, and increasing phosphorylation of eNOS at activation sites Ser-633 and Ser-1177 through AMPK, Akt, and PKA, statins also increase eNOS activity. Lastly, by upregulating GTPCH, statins increase endothelial BH4 availability and restore eNOS coupling. GGPP, geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate; ROCK, Rho-associated protein kinase; GTPCH, guanosine triphosphate cyclohydrolase; AMPK, adenosine monophosphate activated protein kinase; PKA, protein kinase A; PI3K, phosphatidylinositide 3-kinase; ADMA, asymmetric dimethylarginine; EC, endothelial cell. To see this illustration in color, the reader is referred to the web version of this article at www.liebertpub.com/ars